Biological Response Tools
Tools and Frameworks Available to Support Remediation Activities Associated with Wide-Area Sampling in a Biological Incident
A large-scale release of a biological agent can result in contamination of a wide area and would require significant time and resources for recovery. There are several decision support tools and frameworks that decision makers, scientists, and responders can access that will enable more efficient and informed decision making and enhance remediation planning, coordination, and recovery efforts. The purpose of this resource is to provide an inventory of decision support tools and frameworks that are utilized during remediation activities related to sampling design and implementation during a wide-area biological contamination incident. EPA gathered key attributes for each tool or framework (including applicable remediation activity and required inputs for running the tools and outputs generated). This page is intended to provide a clear understanding of the relationship among the currently available tools/frameworks and remediation activities that relate consequence management and implementation, and to map the relationship and sequence of tools/frameworks used during sampling, decontamination, and waste activities in a wide-area biological incident.
The diagram below maps the inputs and outputs for each tool or framework and illustrates the relationship and sequence of tools (blue boxes) and frameworks (green boxes) for supporting wide-area sampling strategies and designs. The diagram illustrates the progression through the various remediation activities (dispersion modeling, operational support, sampling and analysis, data acquisition and management, and data analysis and visualization) and connects each phase with the available support tools.
Scroll down to view the tools and frameworks, including a summary and links to access, or use the navigation links on the right side of the screen to jump to the tools categories.
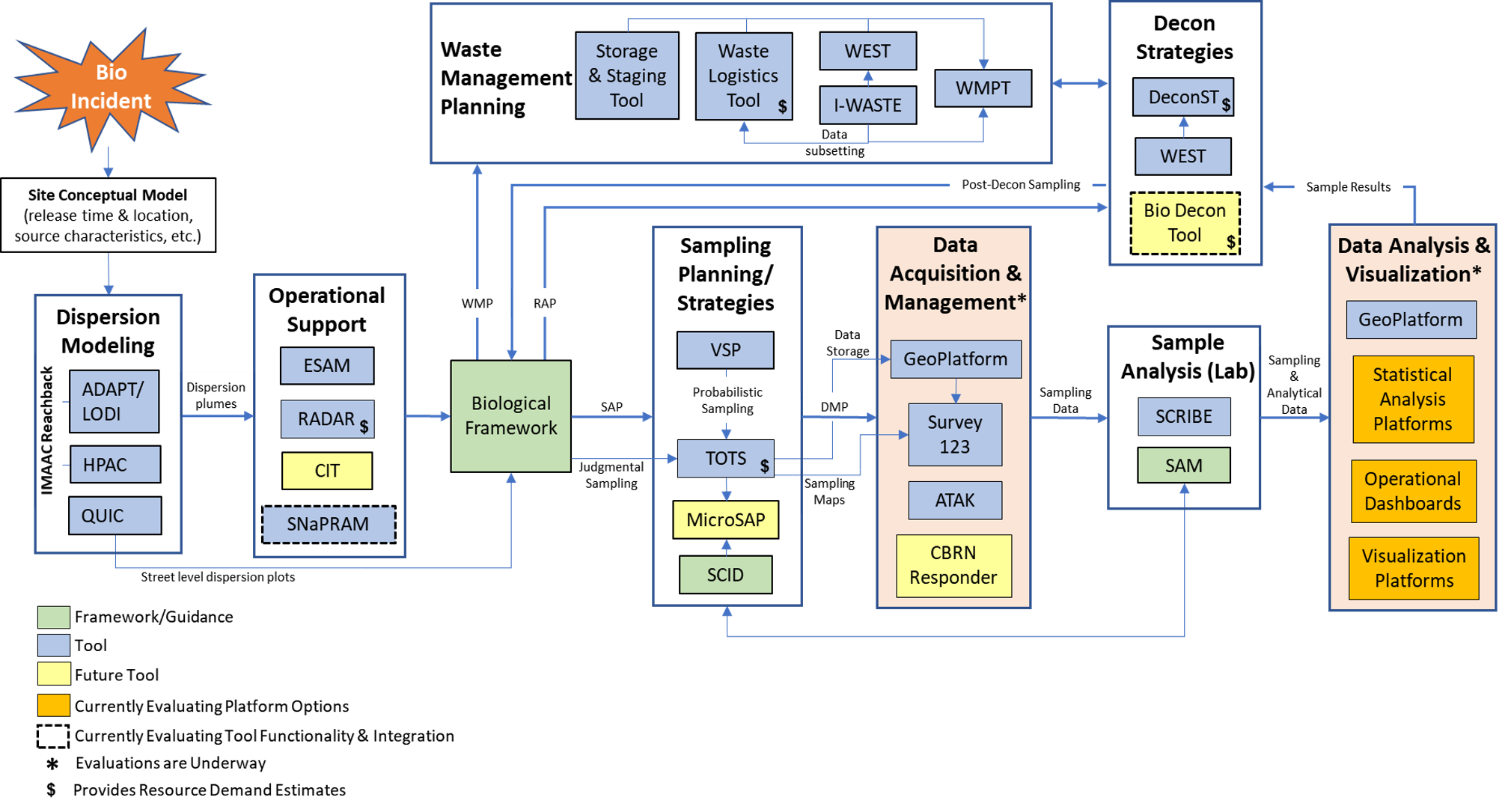
This following section provides a summary of the tools and frameworks identified for each remediation activity, including links for accessing additional information.
Dispersion Modeling
Atmospheric Data Assimilation and Parameterization Tool/Lagrangian Operational Dispersion Integrator (ADAPT/LODI)
ADAPT/LODI is currently used as an operational model within National Atmospheric Release Advisory Center (NARAC) for Interagency Modeling and Atmospheric Assessment Center (IMAAC) reachback. It is a 3-D, Lagrangian Particle Dispersion Model used for various types of chemical, biological, radiological and/or nuclear (CBRN) releases.
Platform: Desktop-based (not released outside of NARAC).
Inputs: Location of the release and source characteristics.
Outputs: Maps of air or ground contamination, dose, and health effects resulting from the release, including protective action zones.
Hazard Prediction and Assessment Capability (HPAC)
HPAC is a CBRN dispersion modeling system that predicts the effects of contamination released into the atmosphere. HPAC is the primary model used by Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA) for IMAAC emergency response plumes. HPAC uses meteorological and geographic information to map potentially contaminated areas. The model assists in estimating response resource requirements and creates customized dispersion plumes and graphs. It can be deployed quickly after the initial request.
Platform: Windows PC with at least 20-25 GB of free hard drive space if the entire archived meteorological data is desired.
Inputs: Time and location (via latitude/longitude selection by map click) of the release; information about the source term.
Outputs: Dispersion plume with estimated hazard zones downwind of the source.
Sample Analysis Tools and Frameworks
Specification Change Review, Implementation, and Baseline Evaluation Board (SCRIBE Board)
Scribe is a desktop-based software tool developed and maintained by EPA’s Environmental Response Team. The tool supports storing and managing sampling, observational and monitoring field data and produces outputs for collected samples and analytical data reports. The interface is flexible and customizable to easily manage and query data. Scribe can import a variety of data and scripts can be saved to manage import mappings. Data generated from an EPA response effort will likely interface with Scribe as part of the overall work and data flow.
Platform: Desktop- and web-based.
Inputs: Data generated from an EPA response effort Maps, sample information.
Outputs: Labels for collected samples, chain-of-custody generation, and analytical lab result data reports.
Selected Analytical Methods for Environmental Remediation and Recovery (SAM)
SAM is an online guidance document query tool that identifies a single analytical method per analyte/matrix pair for use by laboratories performing analyses of environmental samples following a contamination event. SAM provides users with the preferred analytical method available to evaluate the nature and extent of contamination and assess decontamination efficacy.
Platform: Web-based guidance document.
Inputs: Contaminant information.
Outputs: Analytical method information (web-based print to PDF file).
Sampling Planning Tool and Strategy Tools and Frameworks
EPA Biological Agent Field Guidebook
The Biological Agent Field Guidebook is an EPA guidance document that provides the latest scientific, policy, and operational information to support field-level tactics development during the consequence management phase of a biological incident. More specifically, it provides On-Scene Coordinators (OSCs) with existing relevant information on response to biological agents in one document and promotes consistent application of scientific and technical information, guidance, policy, and technology across EPA. This Guidebook predominantly focuses on response to a release of Bacillus anthracis (B. anthracis), but the procedures and information presented can also be useful in responding to incidents involving other biological agents. It will guide responders in the development of several planning documents, including the Sampling and Analysis Plan (SAP), Data Management Plan (DMP), Remedial Action Plan (RAP), and Waste Management Plan (WMP).
Platform: Web-based guidance document.
Inputs: Incident-specific information.
Outputs: Response guidance.
More information (coming soon)
Visual Sample Plan (VSP)
VSP is a software tool developed by Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) that supports the development of a defensible sampling plan based on statistical sampling theory and the statistical analysis of sample results to support confident decision making. VSP couples site, building, and sample location visualization capabilities with optimal sampling design and statistical analysis strategies. VSP generates probabilistic sampling plans based on user input including sampling areas, sample size and the desired statistical specifications. These plans can be used to support decisions regarding sample placement and quantities for characterization and clearance sampling designs.
Platform: Desktop-based.
Inputs: Site map, building footprints, etc.
Outputs: Statistical analysis strategies (sample location and quantities).
Trade-off Tool for Sampling (TOTS)
TOTS is a web-based tool that allows users to create sampling designs and estimating the associated resource demand through an interactive, point-and-click interface for developing biological sampling plans. Users can plot sample locations in conjunction with externally developed indoor or outdoor imagery that can be imported into the tool. Based on the plans designed, TOTS estimates the total time and cost necessary for implementation, which includes sampling kit preparation, conducting the sampling campaign, and lab analysis. The resulting sample plan can be used to consider trade-offs in one’s sampling design (i.e., cost-benefit analysis), alternate sampling approaches (i.e., traditional vs. innovative sampling methods), and sampling coverage.
Platform: Web-based.
Inputs: Map input from ArcGIS; Probabilistic (VSP) and Judgemental/Targeted (user-defined) sample designs.
Outputs: Sampling strategy resource demand estimates (Excel file) and sampling maps (images).
More information (coming soon)
Access Resource/GitHub
Microbiological Sampling and Analysis Plans Tool (MicroSAP)
The MicroSAP Tool is currently under development by EPA and will provide a user-friendly, online tool to assist users in creating a SAP for a microbiological contamination incident while ensuring data are collected of sufficient quality for the intended purpose. The tool will store the SAPs in an online database so they can easily be found and reused or edited as needed. MicroSAP does not replace use of a statistician or other sample planning tools to determine sample numbers or locations. While in development, users can refer to interim SAP Template and accompanying SAP considerations guidance document for SAP resources.
Platform: Document-based (present); Web-based (future.
Inputs: Incident-specific user data.
Outputs: Sampling and Analysis Plan (PDF file) and Summary of DQOs (PDF file).
More information
Access Resource/GitHub (coming soon)
Sample Collection Information Document (SCID)
SCIDs are online guidance documents that provide general information (listed by contaminant) that EPA staff and contractors can use when they collect samples as part of environmental remediation following an intentional or accidental homeland security-related contamination incident. Users can also access the associated information in the query tool located on the ESAM website by searching for the analyte of interest. The information is provided to support general information on sample sizes, containers, shipping and preservation needed to process samples while the collecting samples which are to be analyzed using the specific methods and procedures listed in EPA’s SAM.
Platform: Web-based guidance document.
Inputs: Contaminant information.
Outputs: General information for collection of samples that are to be analyzed using SAM.
.
Operational Support
Environmental Sampling and Analytical Methods (ESAM)
ESAM is a comprehensive program to facilitate a coordinated response following an intentional or accidental homeland security-related contamination incident. The ESAM website provides information that supports field (sample collection methods) and laboratory (sample analysis methods) efforts to characterize contaminated sites and to remediate contamination. Ensuring that responders and labs are using the same techniques is critical so that decision makers have the correct data to plan for remediation and recovery after an incident.
Platform: Web-based.
Inputs: User selects relevant topic.
Outputs: Information for sample collection, analysis, and data management and quality.
RemediAtion DAta Repository (RADAR)
RADAR is a web-based tool that will enable data sharing across EPA’s Homeland Security Research Program's (HSRP’s) models and decision support tools. RADAR consists of a range of topics and information derived from EPA research efforts. The purpose of RADAR is threefold: 1) emergency support: provide support to cleanup and recovery operations; 2) research: inform research and facilitate use of results; and 3) data reuse: provide models and software tools with the most up-to-date research data from a centralized source. The tool is intended for a wide audience including scientists, engineers, and researchers.
Platform: Web-based.
Inputs: User-submitted data.
Outputs: Outputs vary based on user selection (CSV file, MS Excel file, API format and web services for a subset of data; tabular-based).
Stochastic Infrastructure Remediation Model (SIRM)
The SIRM is another forthcoming tool that allows for a series of interconnected infrastructure sectors to be modeled and considers the realistic variability of the impact of a CBRN event. The SIRM considers each of the infrastructure sectors as an operating efficiency percentage and models the restoration of services in each sector as a set of reactions that use resources from other infrastructure sectors to restore services in another sector. This process dynamically models the time required to repair infrastructure sectors, while also allowing the user to consider changes in resource allocation based on user-defined repair factors.
Platform: Desktop-based.
Inputs: Initial sector efficiency, initial contaminated infrastructure; infrastructure coefficients (included with tool).
Outputs: Infrastructure operating efficiency, recovery time, sensitivity analysis (CSV file, PDF file).
More information (coming soon)
Access Resource/GitHub
Sampler Network Performance for Resuspended Aerosols Model (SNaPRAM)
SNaPRAM is a modular model used to assess the effectiveness and cost of a bioaerosol sampler network which can be used to monitor B. anthracis airborne spore concentrations during remediation activities following a large-scale biological incident. The model was initially developed to evaluate the feasibility of filter-based air samplers (low-flow, high-flow, and building air intake filters) to maximize spore detection in the air from resuspension while balancing sampling cost. User selected release scenarios, geographic locations (meteorology and topography) and dispersion models can be used within the SNaPRAM framework.
Platform: Desktop-based.
Inputs: Location, data range to model performance, release characteristics, and boundaries for the bioaerosol sampler network.
Outputs: Number and location of each sampler type that optimizes detection and cost.
More information (coming soon)
Access Resource/GitHub (coming soon)
Data Acquisition and Management Tool
EPA's GeoPlatform/ArcGIS Survey123/Collector/FieldMaps
The EPA GeoPlatform is a shared, EPA technology and governance framework, which encompasses a community of expertise as well as a suite of geospatial tools, data, and web services, including access to tools applicable to data acquisition, management and visualization with an emphasis on geospatial assets. Survey123 is a commercial-off-the-shelf (COTS) form-based application available from Esri that is used for creating, sharing, and analyzing surveys. This application is compatible with geospatial tools and mobile devices (e.g., smart phones and tablets) and improves communication and situational awareness among users. The tool will be evaluated for field data capture and mapping capabilities
Platform: Web-based, mobile, and/or desktop application.
Inputs: Geospatial data, ArcGIS maps, layers and ESRI Collector forms for the area of interest.
Outputs: Geospatial Maps Dashboards, aggregating, sharing , and exporting of field collected data.
Android Team Awareness Kit (ATAK)
ATAK is a communication tool that was developed by the DHS Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) and has been adopted by multiple agencies, including the Department of Defense (DoD). ATAK allows users to submit and receive real-time spatial awareness information and communicate between responders across multiple agencies. ATAK uses Global Positioning System (GPS) and maps that can show elevation and terrain for all responders in the field. Users can drop customizable points or icons, many of which are already pre-programmed in the application, to show their location as well as terrain, weather, and topographical elements. Additionally, users can share encrypted data such as text and photos/videos. Several key attributes include its mobile friendliness across platforms and flexible design to support expansion and customization by different stakeholders.
Platform: Web-based.
Inputs: Maps, spatial awareness information.
Outputs: Cross-agency communication and coordination; sharing of encrypted data such as text and photos/videos.
More information
Access Resource/GitHub
Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and/or Nuclear Responder (CBRNResponder)
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) in collaboration with other federal agencies such as the Department of Energy (DOE) and the EPA are currently developing a tool for incident data sharing and multi-hazard event management, including equipment and personnel, called CBRNResponder. CBRNResponder combines existing tools such as RadResponder, ChemResponder, and BioResponder together to manage all hazards and combine capabilities. However, access to individual tools (e.g., RadResponder and ChemResponder) will still be available. Users can view all events in one location and are provided with a more holistic situational awareness. Additionally, the tool is integrated with federal assets and incorporates national policy into the tools’ design. Some features that will be integrated into the CBRNResponder that already exist in the RadResponder and ChemResponder are plume modeling and geographic information system (GIS) files from NARAC, as well as guidance layers that show monitoring plans and inventories, fixed sensor integration to gain real-time situational awareness with data streams, responder tracking in the field, and access to several databases.
Platform: Web-based, mobile application.
Inputs: Dispersion modeling and GIS files, Incident-specific user data.
Outputs: Rapid support for communication, critical decision making, and operational planning (MS Excel files).
Waste Management Planning Tools
Waste Storage and Staging Site Selection Tool
The Waste Storage and Staging Site Selection Tool is an all-hazards tool that provides a framework for conducting a site selection suitability analysis to identify and rank potential locations for staging and storing waste. Suitability factors considered include soil type, land cover, topography, ease of transportation, and proximity to surface waters to visually identify candidate areas for further evaluation. The tool allows users to leverage other geospatial data to select and save candidate sites for use in planning and/or response efforts.
Platform: Desktop-based.
Inputs: Geospatial data for land use and land cover, slope, surface water, soil group, and roads for a designated area of interest.
Outputs: Candidate staging/storage areas; geodatabase files; tabular data available for export.
More information (coming soon)
Access Resource/GitHub
All-Hazards Waste Logistics Tool
The All-Hazards Waste Logistics Tool supports estimating resource demands associated with transporting large volumes of waste from a disaster-stricken area to waste management facilities. The tool allows users to calculate the cost and time to manage a user-specified quantify of waste; run routing scenarios with user-defined destinations; and to explore options and evaluate constraints to improve preparedness for managing large volumes of waste.
Platform: Desktop-based.
Inputs: Waste quantities and type; waste location and support area.
Outputs: Estimated resource demands (time and costs); MS Excel-based scenario output.
Waste Estimation Support Tool (WEST)
WEST aids emergency planners, responders, and decision makers in analyzing remediation strategies and associated waste management impacts of biological and radiological remediation. WEST implements a systems approach to analyze competing waste management considerations to facilitate rapid and effective remediation that minimizes economic and health impacts to the affected community. The tool provides first order magnitude estimates of waste to illuminate how waste estimates change among decontamination/remediation approaches considered. WEST uses geospatial data to assist in defining the extent of contamination in specified areas.
Platform: Desktop-based.
Inputs: Infrastructure data sets from FEMA's Hazus software and user-created GIS files; plume shape files.
Outputs: Estimated waste types/quantities generated; MS Access and Excel based reporting; KML files that can be exported to Google Earth.
Incident Waste Decision Support Tool (I-WASTE)
I-WASTE is an all-hazards tool that supports planning and response efforts associated with managing waste resulting from incidents of national significance (e.g., contaminated buildings and natural disasters), including estimating waste quantities, identifying waste management facilities, and documenting an incident scenario to facilitate logistics discussions and decision-making. I-WASTE supplies a library of waste management resources to assist in the decision-making process. It offers a searchable database of treatment and disposal facilities including contact information and capacity (where available) on a geographical basis.
Platform: Web-based.
Inputs: Impacted structure types and quantities; treatment and disposal facility types of interest; geographic support area.
Outputs: Estimated waste quantities via Waste Materials Estimator and lists of potential waste management facilities (both MS Excel files).
Waste Management Planning Tool (WMPT)
WMPT assists emergency managers and planners in the public and private sectors in creating or updating a comprehensive plan for managing waste generated from manmade and natural disasters. The tool steps the user through the process for completing sections of a waste management plan and provides links to resources/guidance that address various aspects of the planning process.
Platform: Web-based.
Inputs: Planning input and outputs from other tools.
Outputs: Draft of completed Waste Management Plan in MS Word file.
