Superfund Enforcement FY 2023 Annual Results

The Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA, or commonly known as Superfund) protects communities by ensuring that potentially responsible parties (PRPs) perform or pay for cleanups at Superfund sites and encourages third party investment and reuse of sites. The settlement agreements and orders ensure that potential environmental justice (EJ) concerns from communities overburdened by pollution are addressed and that opportunities for cleanup results in sustainable reuse. In fiscal year (FY) 2023, the Superfund enforcement program continued its mission to protect public health and the environment by cleaning up contamination and returning those properties to productive use when possible, making a visible and lasting difference in all communities, especially those overburdened by pollution.
Superfund enforcement saves taxpayer dollars by negotiating cleanup settlement agreements with PRPs to perform or fund the cleanups. In FY 2023, EPA obtained a total of approximately $988.2 million in commitments from PRPs to cleanup or pay for future site work and EPA obtained $98.8 million for its past costs from cleanup work at 84 Superfund sites. Additionally, EPA billed PRPs approximately $75.5 million for its oversight costs. Fifty-four comfort/status letters were issued to parties interested in reusing and/or redeveloping contaminated, potentially contaminated, and formerly contaminated property supporting the return of Superfund sites to productive use.
FY 2023 accomplishments include:
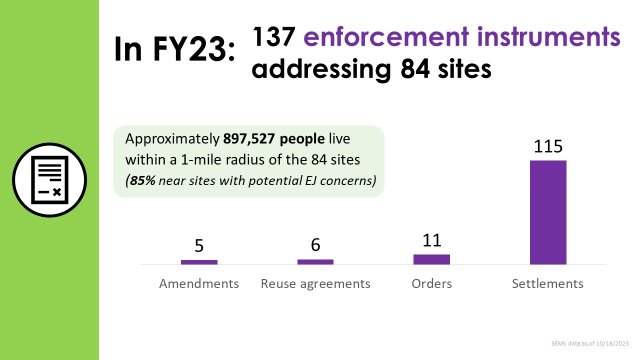
- EPA’s work resulted in 137 enforcement instruments (115 settlements, eleven orders, five settlement amendments, and six reuse agreements) being used at 84 Superfund sites securing site investigations, cleanup, and returning remediated properties to productive reuse.
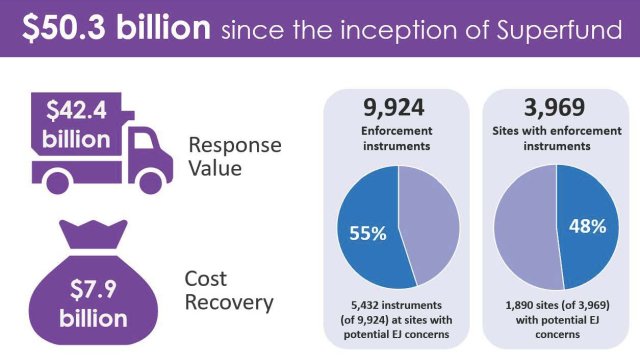
- The approximate value in PRP response and cost recovery commitments is $1.1 billion, where nearly 44% ($481 million) is being spent or reimbursed at sites with potential EJ concerns.
- Finalized Superfund settlement agreements resulted in cleanup in communities where approximately 897,527 people live within a one-mile radius of a Superfund site with 85% (759,373) living in communities with potential EJ concerns.
- 89% of all completed remedial design/remedial action negotiations addressed sites with potential EJ concerns (17 out of 19).
- The value of two unilateral administrative orders (UAOs) rank in the top 10 in the history of the Superfund enforcement program:
- UAO valued at $459.2 million issued to Norfolk Southern to address the East Palestine train derailment ranks second.
- UAO valued at $92.7 million issued to OxyChem for remedial design work at the Diamond Alkali Superfund site ranks eighth.
- With the addition of this fiscal year’s accomplishments, the Superfund enforcement program to date has achieved an estimated value of $50.3 billion in PRP commitments for site cleanup and to reimburse EPA’s costs spent cleaning up sites.
More information on the Superfund enforcement program is available on the Agency’s website.
On this page:
- Highlights of Superfund Enforcement Cleanup Cases
- Superfund Enforcement Furthers EPA’s Environmental Justice Goals
- Prospective Purchaser Agreements Returning Sites to Productive Use
- Incorporating Sustainability, Adaptation, and Resilience into Settlement Agreements
- Superfund Enforcement Cleanup Work Map
Highlights of Superfund Enforcement Cleanup Cases
The following are examples of significant CERCLA settlement agreements finalized in FY 2023.
East Palestine Train Derailment Site Becomes the Second Largest UAO in the Superfund Enforcement Program History

On February 21, 2023, EPA issued a unilateral administrative order (UAO) to Norfolk Southern Railway Company (“Norfolk Southern”) to conduct all necessary response actions associated with the train derailment in East Palestine, Ohio. The UAO requires Norfolk Southern to address the contamination caused by the derailment of its train cars on February 3, 2023, and the following fires. EPA issued the UAO to the railroad for removal cleanup work under CERCLA, which marked the transition of the multi-agency response to the derailment from its “emergency phase” to a longer-term remediation (cleanup) phase. Norfolk Southern excavated and disposed of more than 165,000 tons of contaminated soil and shipped more than 35 million gallons of wastewater off-site benefitting the community. As noted above, the order was one of the largest in the Superfund program’s history, with an estimated value of $459.2 million. More information about the site is available in the press release: EPA Orders Norfolk Southern to Conduct Additional Creek Investigation and Cleanup in East Palestine, Ohio or at the East Palestine Train Derailment site web page.
Settlement Addresses Decades of Copper Smelting Contamination in Soil Around the Anaconda Smelter Superfund Site

At the Anaconda Smelter Superfund site in Butte, Montana, the United States District Court in Butte finalized a consent decree (CD) with Atlantic Richfield on December 16, 2022. Decades of copper smelting activity in the town of Anaconda polluted the soils in yards, commercial and industrial areas, pastures, and open spaces throughout the 300-square-mile Anaconda site. Under the CD, Atlantic Richfield will clean up residential yards in the towns of Anaconda and Opportunity, clean up soils in upland areas above Anaconda and after that, ensure protective closure of the remaining slag piles at the site. This CD follows other important settlements and orders with Atlantic Richfield over the past two decades that have substantially improved the environment and restored valuable natural resources in the Upper Clark Fork basin. This settlement is also the product of a successful federal-state partnership to secure cleanup of a major hazardous waste site. The estimated value of the settlement is approximately $96 million, which includes an estimated $48 million in PRP cleanup work and $48 million for the Agency’s oversight and potential future cleanup costs. More information about the site is available at the Anaconda Smelter Superfund site web page and in the press release: Anaconda, Montana now thriving after more than three decades of clean-up efforts by EPA, State, businesses, and the community.
Order to Clean Up Lower Passaic River Study Area Addresses Highly Contaminated Sediment

On March 2, 2023, EPA issued a UAO directing Occidental Chemical Corporation (OxyChem) to perform the remedial design for the upper nine miles of the Lower Passaic River Study Area of the Diamond Alkali Superfund site in Newark, New Jersey. The interim remedial design work follows EPA’s September 2021 record of decision (ROD) and addresses the highly contaminated sediment that is a source of contamination throughout the river. OxyChem is required to prepare work plans and perform a preliminary investigation, including studies to assess the river bottom, shoreline, and other aspects of the river in preparation for cleanup. The cleanup plan that OxyChem will be designing is an interim action, meaning that when the cleanup has been completed, EPA will evaluate the results and may determine that further work is necessary to address any remaining contamination in this section of the river. It is the eighth largest UAO in Superfund program history with an estimated value of $92.7 million. More information is available in the press release: EPA Orders Occidental Chemical Corp. to Design Cleanup Plan for the Upper Nine Miles of the Lower Passaic River at the Diamond Alkali Superfund Site in New Jersey.
Superfund Enforcement Furthers EPA’s Environmental Justice Goals
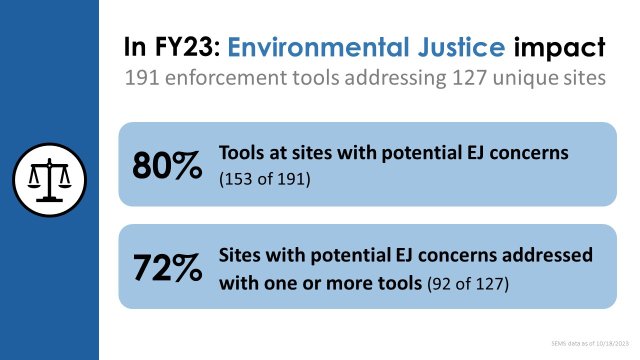
EJ goals continue to be integral to EPA’s mission when conducting Superfund cleanups. Superfund cleanups protect some of the country’s most vulnerable and polluted communities. EPA’s Superfund program focuses on ensuring that people can live and work in healthy and vibrant places. As part of that focus, EPA considers how to incorporate potential EJ concerns throughout the Superfund cleanup process. In FY 2023, 80% of all final Superfund enforcement agreements at sites with potential EJ concerns (109 out of 137 enforcement instruments) helped to provide relief to those communities overburdened by environmental contamination. Further, of the 84 sites with new cleanup work agreements, 68% of those sites are adjacent to communities with potential EJ concerns. Examples of settlement agreements include:
Settlement Investigates Soil and Groundwater Contamination at UPRR Houston Wood Preserving Works Site

On February 27, 2023, Union Pacific Railroad Company (“Union Pacific”) entered into a CERCLA administrative settlement agreement in the Fifth Ward Kashmere Gardens neighborhood of Houston, Texas as part of its work on a RCRA Corrective Action site. Under the agreement the company will conduct approximately $6.9 million in removal assessment work in an overburdened community, as well as pay future response costs. The removal assessment work includes on and off-site soil sampling, vapor intrusion investigations at potentially affected residences, evaluations of the off-site storm sewer system for potential contamination associated with the site, and development of a proposal supporting EPA’s community involvement plan. The site is in a community with potential EJ concerns and was also part of Administrator Reagan’s Journey to Justice Tour to spotlight longstanding environmental justice concerns in historically marginalized communities. More information can be found in the press release: EPA Orders Union Pacific to Assess Contamination in Houston’s Greater Fifth Ward Neighborhood or the Houston Wood Preserving Works Superfund site profile web page.
Settlement Supports Cleanup and Reuse in San Gabriel Valley Community with potential EJ Concerns
On September 29, 2023, EPA and DOJ finalized a BFPPA at the El Monte Operable Unit (EMOU) of the San Gabriel Valley Superfund site located within the cities of El Monte, Temple City, and Rosemead, California. Between 1956 and 2004, Crown City Plating Company operated a plating facility within what is now the EMOU. El Monte SS Properties, LLC (EMSSP) acquired a 10-acre portion of the EMOU, which is a major contributing source of metals and volatile organic compounds to the groundwater. Under the terms of the settlement, EMSSP will perform an estimated $3 million in work to address source contamination at the property, which is located in a community overburdened by environmental pollution and contaminants. EMSSP’s cleanup activities at the property will prevent further contamination of the groundwater, which is a drinking water resource for the community. EMSSP intends to redevelop the property in a manner consistent with the City of El Monte’s zoning, which will benefit the local community through the addition of jobs and an increased tax base. More information can be found at the El Monte Superfund site profile web page or the "Construction of Groundwater Treatment" fact sheet on the El Monte operable unit.
Prospective Purchaser Agreements Returning Sites to Productive Use
In Superfund’s efforts to return sites to productive use, prospective purchase agreements (PPA) and bona fide prospective purchase agreements (BFPPA) are important tools. A PPA is the primary settlement instrument to address the liability concerns of a prospective purchaser or other third party who wants to clean up and reuse a site of federal interest. EPA also uses BFPPAs in some circumstances where appropriate. Both agreements provide liability protection in exchange for the purchaser’s performance of cleanup work and reimbursement of certain EPA costs. EPA worked with the Department of Justice (DOJ) to finalize several of these agreements this fiscal year to support the clean-up and reuse of contaminated properties.
Bona Fide Prospective Purchaser Agreement Addresses Contamination at Superfund Site Located within Mississippi Community

At the Mississippi Phosphates site in Pascagoula, Mississippi, on September 26, 2023, EPA and DOJ finalized a Bona Fide Prospective Purchaser Agreement. The site was used to produce diammonium phosphate fertilizer from the 1950s through 2014 when Mississippi Phosphates Corporation filed for bankruptcy. In 2018, EPA added the site to the Superfund National Priorities List (NPL) and proposed a cleanup plan for portions of the site. Seven Seas Terminals LLC intends to acquire some of the site for use as a dry bulk terminal storage and a tank terminal operation. Under the terms of the settlement, Seven Seas agreed to perform an estimated $10.5M in removal work and ensure continued access for EPA’s additional cleanup activities at other portions of the site. Removal work includes demolition of the sulfuric acid plants, installation of an impermeable cap as a containment control for the area proposed as a tank terminal operation, and sampling of soils under demolished structures and slab. The cleanup and reuse of the site will benefit the surrounding community in Jackson County by creating jobs and increasing the tax base through reuse of the property. More information can be found on Mississippi Phosphate’s Superfund site profile web page or in the press release: EPA announces agreement with prospective purchaser of the former plant at the Mississippi Phosphates Corporation Superfund Site in Pascagoula, Mississippi.
PPA Secures Long-Term Steward to Implement Remedy and Support Reuse in Massachusetts

At the Wells G&H site, in Woburn, Massachusetts, EPA and DOJ finalized a PPA with developers in November 2022. The developers, IV5 60 Olympia Avenue LLC and IV5 60 Olympia Land LLC, intend to reuse a 21-acre parcel within the site as a transportation hub. The PRPs had been performing Superfund removal work under administrative settlement agreements with EPA since 2003 but were unable to complete the work due to their lack of funds. Under the terms of the PPA, the developers agreed to complete a new characterization of the property; submit a work plan for EPA approval; provide $2M in financial assurance; and complete the removal action in a faster and more efficient manner. The PPA also enabled EPA to reach a separate settlement agreement with the PRPs that provided for their payment of $1.2 million from the proceeds of the sale of the parcel towards EPA’s unrecovered past costs. More information can be found at the Wells G&H Superfund site profile web page.
Bona Fide Prospective Purchaser Acquires Property from PRPs and Agrees to Support Cleanup

At Nelson Tunnel/Commodore Waste Rock Superfund Site, located near Creede, Colorado, EPA and DOJ reached a multi-party settlement with three PRPs and a BFPP. Under the agreement, two of the PRPs, Commodore Mining Company and Del Monte Mining Company, will donate 100% and 75%, respectively, of their properties to Mineral County, which will acquire the properties as a BFPP. The third PRP, Kanawha Mines, LLC, will retain its property but waived its right to certain claims under state and federal law concerning certain water rights. Under the agreement, Mineral County will provide for site security, maintenance of the Site access road, and staging of response equipment at the transferred properties that intersect with the Site to support EPA’s implementation of the remedy. The County will also maintain a county ordinance to protect the Site and surrounding areas from mine-impacted contamination. The estimated value of Mineral County’s contributions is $2,025,000. In addition, Mineral County agreed to raise funds necessary to stabilize and preserve several historic mining structures located on the properties that are important to the local community. More information can be found on Nelson Tunnel Superfund site’s web page.
Incorporating Sustainability, Adaptation, and Resilience into Settlement Agreements
In September 2023, EPA’s cleanup enforcement program issued the memorandum “Sustainability in the Cleanup Enforcement Under CERCLA and RCRA” which reinforces EPA’s positions on sustainability in settlement agreements by:
- Encouraging cleanup enforcement staff to collaborate with their program office counterparts to incorporate applicable principles; and
- Describing the identified seven sustainability principles; and
- Providing information on these topics in a centralized location.

The memorandum includes a compendium of case highlights that incorporate the seven sustainability principles and a spreadsheet, referred to as the Sustainability Resource Library, which provides detailed information and links to federal and other external resources related to the seven principles. The principles of sustainability span multiple cleanup programs, reflect a developing set of human health and environmental protection practices, and help achieve the Agency’s goals and priorities of protecting human health and the environment. This can help protect vulnerable populations, facilitate economic development, and provide long term stewardship of the land, among other things. Going forward, EPA will continue to review cleanup enforcement tools to find opportunities that makes it easier for the Agency’s regional enforcement personnel, working with their program partners, to incorporate sustainability principles at sites.
Superfund Enforcement Cleanup Work Map
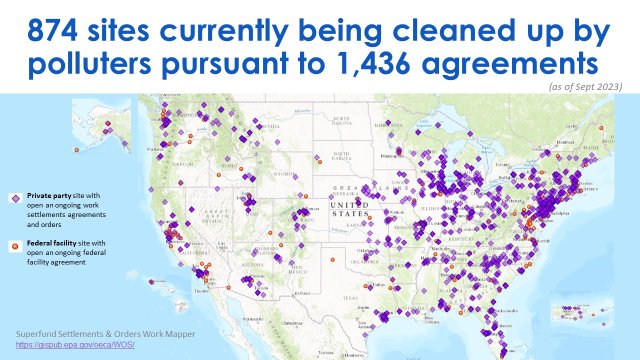
EPA's Superfund Settlements and Work Order Mapper highlights the current cleanup work taking place at privately and federally owned Superfund sites across the country resulting from the Agency’s enforcement work to negotiate cleanup settlement agreements or issued orders. The data is current through September 30, 2023.
The map contains data on the cleanup work at 874 sites under 1,436 enforcement agreements and orders valued at more than 24.6 billion in estimated cleanup costs.
Visit the Information about the Superfund Cleanup Work Map web page for the map’s data overview, disclaimer language, and user guide
