Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is the last of the chain of Great Lakes that straddle the Canada/United States border. Since Lake Ontario is the downstream Great Lake, it is impacted by human activities occurring throughout the Lake Superior, Michigan, Huron, and Erie basins.
About Lake Ontario
- second smallest by volume
- average depth 283 ft. (86m)
- retention time = 6 years (a measure based on the volume of water in the lake and the mean rate of outflow)
- urban industrial centers (Hamilton and Toronto) on the Canadian side
- U.S. shore is less urbanized, not intensively farmed
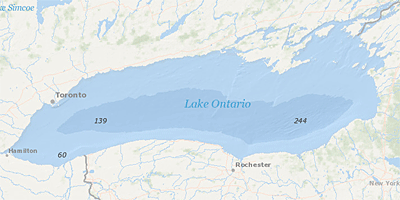
NOAA Image Measurement of Depth of Water in Lake Ontario
Environmental Issues
There are several major issues affecting the health of Lake Ontario:
The following links exit the site
- Degradation of the lower food chain
- Loss of biodiversity
- Fish consumption restrictions
- Aquatic invasive species
- Nearshore water quality
- Lake Ontario LAMPS and Associated Reports
- Lake Ontario Great Lakes Areas of Concern (AOCs)
- Eighteenmile Creek AOC - New York
- Niagara River AOC - New York
- Oswego River AOC - New York DELISTED
- Rochester Embayment AOC - New York
- St. Lawrence River AOC - New York and St. Lawrence River AOC - Canada
- Hamilton Harbour AOC - Canada
- Toronto and Region AOC - Canada
- Port Hope Harbour AOC - Canada
- Bay of Quinte AOC - Canada
- Great Lakes Restoration Initiative Grants
-
Paul Smith's College of Arts and Sciences ($499,816) for invasive species prevention
-
- Lake Ontario Tributaries: 2009-2010 Field Data Report March 2011
- Niagara River Toxics Management Plan Annual Status Reports
- Niagara River Toxics Management Plan Progress Reports and Work Plans
