Mold Remediation in Schools and Commercial Buildings Guide: Chapter 3
Investigating, Evaluating and Remediating Moisture and Mold Problems
The content on this web page is based on the publication Mold Remediation in Schools and Commercial Buildings[EPA 402-K-01-001, Reprinted September 2008]. Updates have been made to some resources and links.
In This Guide:
Investigating, Evaluating and Remediating Moisture and Mold Problems
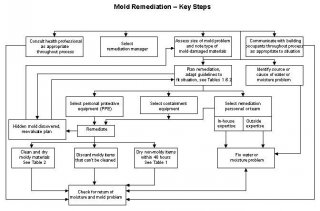
- Mold Remediation - Key Steps
- Plan the Remediation Before Starting Work
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air-Conditioning (HVAC) System
- Hidden Mold
- Remediation
- Table 1: Water Damage Cleanup and Mold Prevention
- Table 2: Mold Remediation Guidelines
- Cleanup Methods
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Containment
- Equipment
- Sampling
- How Do You Know When You Have Finished Remediation/Cleanup?
- Footnotes
- Do not touch mold or moldy items with bare hands.
- Do not get mold or mold spores in your eyes.
- Do not breathe in mold or mold spores.
- Consult Table 2 and text for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and containment guidelines.
- Consider using PPE when disturbing mold. The minimum PPE is an N-95 respirator, gloves and eye protection.
Mold Remediation - Key Steps
- Consult health professional as appropriate throughout process
- Select remediation manager
- Assess size of mold problem and note type of mold-damaged materials
- Communicate with building occupants throughout process as appropriate to situation
- Identify source or cause of water or moisture problem
- Plan remediation, adapt guidelines to fit situation, see Table 1 Table 2
- Select personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Select containment equipment
- Select remediation personnel or team
- Choose between outside expertise or in-house expertise
- Remediate
- Fix water or moisture problem
- Clean and dry moldy materials See Table 2
- Discard moldy items that can't be cleaned
- Dry non-moldy items within 48 hours See Table 1
- Check for return of moisture and mold problem
- If hidden mold is discovered, reevaluate plan
Mold Areas Encountered During an Investigation
Plan the Remediation Before Starting the Work
Remediation Plan
Assess the size of the mold and/or moisture problem and the type of damaged materials before planning the remediation work. Select a remediation manager for medium or large jobs (or small jobs requiring more than one person). The remediation plan should include steps to fix the water or moisture problem, or the problem may reoccur. The plan should cover the use of appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and include steps to carefully contain and remove moldy building materials to avoid spreading the mold.(2) A remediation plan may vary greatly depending on the size and complexity of the job, and may require revision if circumstances change or new facts are discovered.
The remediation manager's highest priority must be to protect the health and safety of the building occupants and remediators. It is also important to communicate with building occupants when mold problems are identified.(3) In some cases, especially those involving large areas of contamination, the remediation plan may include temporary relocation of some or all of the building occupants.
The decision to relocate occupants should consider:
- The size and type of the area affected by mold growth
- The type and extent of health effects reported by the occupants
- The potential health risks that could be associated with debris
- The amount of disruption likely to be caused by remediation activities
If possible, remediation activities should be scheduled during off-hours when building occupants are less likely to be affected.
Remediators, particularly those with health-related concerns, may wish to check with their doctors or health care professionals before working on mold remediation or investigating potentially moldy areas. If you have any doubts or questions, you should consult a health professional before beginning a remediation project.
Heating, Ventilation, and Air-Conditioning (HVAC) System
Do not run the HVAC system if you know or suspect that it is contaminated with mold. If you suspect that it may be contaminated (it is part of an identified moisture problem, for instance, or there is mold growth near the intake to the system), consult,
- EPA's guide Should You Have the Air Ducts in Your Home Cleaned? (4)
- Resources List in this Guide
Hidden Mold
In some cases, indoor mold growth may not be obvious. It is possible that mold may be growing on hidden surfaces, such as:
- The back side of dry wall
- Wallpaper
- Paneling
- The top of ceiling tiles
- The underside of carpets and pads
Possible locations of hidden mold can include:
- Pipe chases and utility tunnels (with leaking or condensing pipes)
- Walls behind furniture (where condensation forms)
- Condensate drain pans inside air handling units
- Porous thermal or acoustic liners inside ductwork
- Roof materials above ceiling tiles (due to roof leaks or insufficient insulation)
Some building materials, such as dry wall with vinyl wallpaper over it or wood paneling, may act as vapor barriers, (5) trapping moisture underneath their surfaces and thereby providing a moist environment where mold can grow. You may suspect hidden mold if a building smells moldy, but you cannot see the source, or if you know there has been water damage and building occupants are reporting health problems. Investigating hidden mold problems may be difficult and will require caution when the investigation involves disturbing potential sites of mold growth—make sure to use personal protective equipment (PPE). For example, removal of wallpaper can lead to a massive release of spores from mold growing on the underside of the paper. If you believe that you may have a hidden mold problem, you may want to consider hiring an experienced professional. If you discover hidden mold, you should revise your remediation plan to account for the total area affected by mold growth.
Remediation
- Fix the water or humidity problem. Complete and carry out repair plan if appropriate. Revise and/or carry out maintenance plan if necessary. Revise remediation plan as necessary, if more damage is discovered during remediation. For additional information see:
- Mold Remediation - Key Steps
- Resources List
- Continue to communicate with building occupants, as appropriate to the situation. Be sure to address all concerns.
- Completely clean up mold and dry water-damaged areas. Select appropriate cleaning and drying methods for damaged/contaminated materials. Carefully contain and remove moldy building materials. Use appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE). Arrange for outside professional support if necessary.
Table 1: Water Damage Cleanup and Mold Prevention (6)
Table 1 presents strategies to respond to water damage within 24-48 hours. These guidelines are designed to help avoid the need for remediation of mold growth by taking quick action before growth starts. If mold growth is found on the materials listed in Table 1, refer to Table 2 for guidance on remediation. Depending on the size of the area involved and resources available, professional assistance may be needed to dry an area quickly and thoroughly. See:
- Table 1
- Table 2
Table 2: Mold Remediation Guidelines (7)
Table 2 presents remediation guidelines for building materials that have or are likely to have mold growth. The guidelines in Table 2 are designed to protect the health of occupants and cleanup personnel during remediation. These guidelines are based on the area and type of material affected by water damage and/or mold growth. Please note that these are guidelines; some professionals may prefer other cleaning methods. See Table 2
If you are considering cleaning your ducts as part of your remediation plan, you should consult EPA's publication entitled, "Should You Have the Air Ducts In Your Home Cleaned?" (8). If possible, remediation activities should be scheduled during off-hours when building occupants are less likely to be affected. See:
- Should You Have the Air Ducts In Your Home Cleaned?
- Resources List
Although the level of personal protection suggested in these guidelines is based on the total surface area contaminated and the potential for remediator and/or occupant exposure, professional judgment should always play a part in remediation decisions. These remediation guidelines are based on the size of the affected area to make it easier for remediators to select appropriate techniques, not on the basis of health effects or research showing there is a specific method appropriate at a certain number of square feet. The guidelines have been designed to help construct a remediation plan. The remediation manager will then use professional judgment and experience to adapt the guidelines to particular situations. When in doubt, caution is advised. Consult an experienced mold remediator for more information.
A more cautious or conservative approach to remediation is indicated in cases in which:
- A particularly toxic mold species has been identified or is suspected
- When extensive hidden mold is expected (such as behind vinyl wallpaper or in the HVAC system)
- When the chances of the mold becoming airborne are estimated to be high
- Sensitive individuals (e.g., those with severe allergies or asthma) are present
Always make sure to protect remediators and building occupants from exposure to mold.
Cleanup Methods
Mold can eventually cause structural damage to a school or large building, if a mold/moisture problem remains unaddressed for a long time. In the case of a long-term roof leak, for example, molds can weaken floors and walls as the molds feed on wet wood. If you suspect that mold has damaged building integrity, you should consult a structural engineer or other professional with expertise in this area.
A variety of mold cleanup methods are available for remediating damage to building materials and furnishings caused by moisture control problems and mold growth. The specific method or group of methods used will depend on the type of material affected, as presented in Table 2. Please note that professional remediators may use some methods not covered in these guidelines; absence of a method in the guidelines does not necessarily mean that it is not useful. (9). See Table 2
Method 1: Wet Vacuum
Wet vacuums are vacuum cleaners designed to collect water. They can be used to remove water from floors, carpets and hard surfaces where water has accumulated. They should not be used to vacuum porous materials, such as gypsum board. They should be used only when materials are still wet — wet vacuums may spread spores if sufficient liquid is not present. The tanks, hoses and attachments of these vacuums should be thoroughly cleaned and dried after use since mold and mold spores may stick to the surfaces.
Method 2: Damp Wipe
Whether dead or alive, mold is allergenic, and some molds may be toxic. Mold can generally be removed from nonporous (hard) surfaces by wiping or scrubbing with water, or water and detergent. It is important to dry these surfaces quickly and thoroughly to discourage further mold growth. Instructions for cleaning surfaces, as listed on product labels, should always be read and followed. Porous materials that are wet and have mold growing on them may have to be discarded. Since molds will infiltrate porous substances and grow on or fill in empty spaces or crevices, the mold can be difficult or impossible to remove completely.
Method 3: HEPA Vacuum
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) vacuums are recommended for final cleanup of remediation areas after materials have been thoroughly dried and contaminated materials removed. HEPA vacuums are also recommended for cleanup of dust that may have settled on surfaces outside the remediation area. Care must be taken to assure that the filter is properly seated in the vacuum so that all the air must pass through the filter. When changing the vacuum filter, remediators should wear PPE to prevent exposure to the mold that has been captured. The filter and contents of the HEPA vacuum must be disposed of in well-sealed plastic bags.
Method 4: Discard — Remove Damaged Materials and Seal in Plastic Bags
Building materials and furnishings that are contaminated with mold growth and are not salvageable should be double-bagged using 6-mil polyethylene sheeting. These materials can then usually be discarded as ordinary construction waste. It is important to package mold-contaminated materials in sealed bags before removal from the containment area to minimize the dispersion of mold spores throughout the building. Large items that have heavy mold growth should be covered with polyethylene sheeting and sealed with duct tape before they are removed from the containment area.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
If the remediation job disturbs mold and mold spores become airborne, then the risk of respiratory exposure goes up. Actions that are likely to stir up mold include:
- Breakup of moldy porous materials such as wallboard
- Invasive procedures used to examine or remediate mold growth in a wall cavity
- Actively stripping or peeling wallpaper to remove it
- Using fans to dry items
The primary function of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is to avoid inhaling mold and mold spores and to avoid mold contact with the skin or eyes. The following sections discuss the different types of PPE that can be used during remediation activities. Please note that all individuals using certain PPE equipment, such as half-face or full-face respirators, must be trained, must have medical clearance and must be fit-tested by a trained professional. In addition, the use of respirators must follow a complete respiratory protection program as specified by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration. For more information see Resources List.
Skin and Eye Protection
Gloves are required to protect the skin from contact with mold allergens (and in some cases mold toxins) and from potentially irritating cleaning solutions. Long gloves that extend to the middle of the forearm are recommended. The glove material should be selected based on the type of materials being handled. If you are using a biocide (such as chlorine bleach) or a strong cleaning solution, you should select gloves made from:
- Natural rubber
- Neoprene
- Nitrile
- Polyurethane
- PVC
If you are using a mild detergent or plain water, ordinary household rubber gloves may be used. To protect your eyes, use properly fitted goggles or a full-face respirator with HEPA filter. Goggles must be designed to prevent the entry of dust and small particles. Safety glasses or goggles with open vent holes are not acceptable.
Respiratory Protection
Respirators protect cleanup workers from inhaling airborne mold, mold spores and dust.
- Minimum: When cleaning up a small area affected by mold, you should use an N-95 respirator. This device:
- Covers the nose and mouth
- Will filter out 95% of the particulates in the air
- Is available in most hardware stores
- Limited: Limited PPE includes use of a half-face or full-face air purifying respirator (APR) equipped with a HEPA filter cartridge. These respirators contain both inhalation and exhalation valves that filter the air and ensure that it is free of mold particles. Note that half-face APRs do not provide eye protection. In addition, the HEPA filters do not remove vapors or gases. You should always use respirators approved by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. See Resources List.
- Full: In situations in which high levels of airborne dust or mold spores are likely or when intense or long-term exposures are expected (e.g., the cleanup of large areas of contamination), a full-face, powered air purifying respirator (PAPR) is recommended. Full-face PAPRs use a blower to force air through a HEPA filter. The HEPA-filtered air is supplied to a mask that covers the entire face or a hood that covers the entire head. The positive pressure within the hood prevents unfiltered air from entering through penetrations or gaps. Individuals must be trained to use their respirators before they begin remediation. The use of these respirators must be in compliance with OSHA regulations. See Resources List.
Disposable Protective Clothing
Disposable clothing is recommended during a medium or large remediation project to prevent the transfer and spread of mold to clothing and to eliminate skin contact with mold.
- Limited: Disposable paper overalls can be used.
- Full: Mold-impervious disposable head and foot coverings, and a body suit made of a breathable material, such as TYVEK®, should be used. All gaps, such as those around ankles and wrists, should be sealed (many remediators use duct tape to seal clothing).
Containment
The purpose of containment during remediation activities is to limit release of mold into the air and surroundings, in order to minimize the exposure of remediators and building occupants to mold. Mold and moldy debris should not be allowed to spread to areas in the building beyond the contaminated site.
The two types of containment recommended in Table 2 are limited and full. The larger the area of moldy material, the greater the possibility of human exposure and the greater the need for containment. In general, the size of the area helps determine the level of containment. However, a heavy growth of mold in a relatively small area could release more spores than a lighter growth of mold in a relatively large area. Choice of containment should be based on professional judgment.(10) The primary object of containment should be to prevent occupant and remediator exposure to mold. See Table 2
Limited Containment
Limited containment is generally recommended for areas involving between 10 and 100 square feet (ft2) of mold contamination. The enclosure around the moldy area should consist of a single layer of 6-mil, fire-retardant polyethylene sheeting. The containment should have a slit entry and covering flap on the outside of the containment area. For small areas, the polyethylene sheeting can be affixed to floors and ceilings with duct tape. For larger areas, a steel or wooden stud frame can be erected and polyethylene sheeting attached to it. To minimize the migration of contaminants to other parts of the building, certain places within the containment area must be sealed with polyethylene sheeting, including:
- All supply and air vents
- Doors
- Chases
- Risers
Heavy mold growth on ceiling tiles may impact HVAC systems if the space above the ceiling is used as a return air plenum. In this case, containment should be installed from the floor to the ceiling deck, and the filters in the air handling units serving the affected area may have to be replaced once remediation is finished.
The containment area must be maintained under negative pressure relative to surrounding areas. This will ensure that contaminated air does not flow into adjacent areas. This can be done with a HEPA-filtered fan unit exhausted outside of the building. For small, easily contained areas, an exhaust fan ducted to the outdoors can also be used. The surfaces of all objects removed from the containment area should be remediated/cleaned prior to removal. The remediation guidelines outlined in Table 2 can be implemented when the containment is completely sealed and is under negative pressure relative to the surrounding area. See Table 2
Full Containment

Full containment is recommended for the cleanup of mold-contaminated surface areas greater than 100 ft2 or in any situation in which it appears likely that the occupant space would be further contaminated without full containment. Double layers of polyethylene should be used to create a barrier between the moldy area and other parts of the building. A decontamination chamber or airlock should be constructed for entry into and exit from the remediation area. The entryways to the airlock from the outside and from the airlock to the main containment area should consist of a slit entry with covering flaps on the outside surface of each slit entry. The chamber should be large enough to hold a waste container and allow a person to put on and remove PPE. All contaminated PPE, except respirators, should be placed in a sealed bag while in this chamber. Respirators should be worn until remediators are outside the decontamination chamber. PPE must be worn throughout the final stages of HEPA vacuuming and damp-wiping of the contained area. PPE must also be worn during HEPA vacuum filter changes or cleanup of the HEPA vacuum.
Equipment
Moisture Meters: Measure/Monitor Moisture Levels in Building Materials

Moisture meters may be helpful for measuring the moisture content in a variety of building materials following water damage. They can also be used to monitor the process of drying damaged materials. These direct reading devices have a thin probe which can be inserted into the material to be tested or can be pressed directly against the surface of the material. Moisture meters can be used on materials such as carpet, wallboard, wood, brick and concrete.
Humidity Gauges or Meters: Monitor Moisture Levels in the Air
Humidity meters can be used to monitor humidity indoors. Inexpensive ($50) models are available that monitor both temperature and humidity.
Humidistat: Turns on HVAC System at Specific Relative Humidity (RH)
A humidistat is a control device that can be connected to the HVAC system and adjusted so that, if the humidity level rises above a set point, the HVAC system will automatically come on.
HVAC System Filter: Filters Outdoor Air
Use high-quality filters in your HVAC system during remediation. Consult an engineer for the appropriate efficiency for your specific HVAC system and consider upgrading your filters if appropriate. Conventional HVAC filters are typically not effective in filtering particles the size of mold spores. Consider upgrading to a filter with a minimum efficiency of 50 to 60% or a rating of MERV 8, as determined by Test Standard 52.2 of the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers. Remember to change filters regularly and change them following any remediation activities.
Sampling
Is sampling for mold needed? In most cases, if visible mold growth is present, sampling is unnecessary. You may consider sampling as part of your site evaluation in specific instances, such as:
- Cases where litigation is involved
- The source(s) of the mold contamination is unclear
- Health concerns are a problem
Surface sampling may also be useful in order to determine if an area has been adequately cleaned or remediated. Sampling should be done only after developing a sampling plan that includes a confirmable theory regarding suspected mold sources and routes of exposure. Figure out what you think is happening and how to prove or disprove it before you sample.
If you do not have extensive experience and/or are in doubt about sampling, consult an experienced professional. This individual can help you decide if sampling for mold is useful and/or needed, and will be able to carry out any necessary sampling. It is important to remember that the results of sampling may have limited use or application. Sampling may help locate the source of mold contamination, identify some of the mold species present and differentiate between mold and soot or dirt. Pre- and post-remediation sampling may also be useful in determining whether remediation efforts have been effective. After remediation, the types and concentrations of mold in indoor air samples should be similar to what is found in the local outdoor air. Since no EPA or other Federal threshold limits have been set for mold or mold spores, sampling cannot be used to check a building's compliance with Federal mold standards.
Sampling for mold should be conducted by professionals with specific experience in designing mold sampling protocols, sampling methods and interpretation of results. Sample analysis should follow analytical methods recommended by the American Industrial Hygiene Association (AIHA), the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH), or other professional guidelines (see Resources List). Types of samples include:
- Air samples
- Surface samples
- Bulk samples (chunks of carpet, insulation, wall board, etc.)
- Water samples from condensate drain pans or cooling towers
A number of pitfalls may be encountered when inexperienced personnel conduct sampling:
- They may take an inadequate number of samples
- There may be inconsistency in sampling protocols
- The samples may become contaminated
- Outdoor control samples may be omitted
- You may incur costs for unneeded or inappropriate samples
Budget constraints will often be a consideration when sampling; professional advice may be necessary to determine if it is possible to take sufficient samples to characterize a problem on a given budget. If it is not possible to sample properly, with a sufficient number of samples to answer the question(s) posed, it would be preferable not to sample. Inadequate sample plans may generate misleading, confusing and useless results.
Keep in mind that air sampling for mold provides information only for the moment in time in which the sampling occurred, much like a snapshot. Air sampling will reveal, when properly done, what was in the air at the moment when the sample was taken. For someone without experience, sampling results will be difficult to interpret. Experience in interpretation of results is essential.
Footnotes:
2. Molds are known allergens and may be toxic. You may wish to use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) while investigating a mold problem, as well as during remediation/clean-up situations. The minimum PPE includes an N-95 respirator, gloves, and eye protection.
3. See Appendix C.
4. Although this document has a residential focus, it is applicable to other building types.
5. Resources List has more information on vapor barriers and building construction. It is important that building materials be able to dry; moisture should not be trapped between two vapor barriers or mold may result. See Resources List
6. Please note that Table 1 and Table 2 contain general guidelines. Their purpose is to provide basic information for remediation managers to first assess the extent of the damage and then to determine whether the remediation should be managed by in-house personnel or outside professionals. The remediation manager can then use the guidelines to help design a remediation plan or to assess a plan submitted by outside professionals. See:
- Table 1
- Table 2
7. Please note that Table 1 and Table 2 contain general guidelines. Their purpose is to provide basic information for remediation managers to first assess the extent of the damage and then to determine whether the remediation should be managed by in-house personnel or outside professionals. The remediation manager can then use the guidelines to help design a remediation plan or to assess a plan submitted by outside professionals. See:
- Table 1
- Table 2
8. Although this document has a residential focus, it is applicable to other building types.
9. If you are unsure what to do, or if the item is expensive or of sentimental value, you may wish to consult a specialist. Specialists commonly listed in phone books include:
- Furniture repair/restoration
- Painting
- Art restoration and conservation
- Carpet and rug cleaning
- Water damage
- Fire/water restoration
Be sure to ask for and check references; look for affiliation with professional organizations. See Resources List.
10. For example, a remediator may decide that a small area that is extensively contaminated and has the potential to distribute mold to occupied areas during cleanup should have full containment, whereas a large wall surface that is lightly contaminated and easily cleaned would require only limited containment.