Acid Rain Program Results
The Acid Rain Program (ARP) has delivered significant reductions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOX) emissions from fossil fuel-fired power plants, extensive environmental and human health benefits, and far lower-than-expected costs. Together with more recent power sector regulations, including the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAPR) programs, and a rapidly changing energy sector, the ARP has helped deliver annual SO2 reductions of over 95% and annual NOX emissions reductions of over 89%. The Power Plant Emissions Reductions page has maps and data highlighting these emissions reductions, and the Power Sector Programs Progress Report provide an annual overview of program features and results, from compliance to air quality impacts.
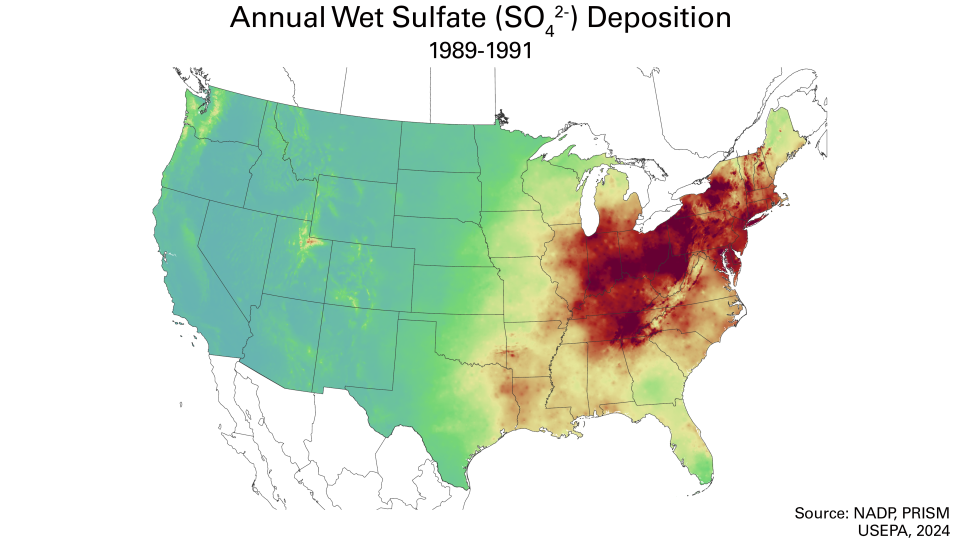
Swipe left and right over the maps to see the changes before and after.
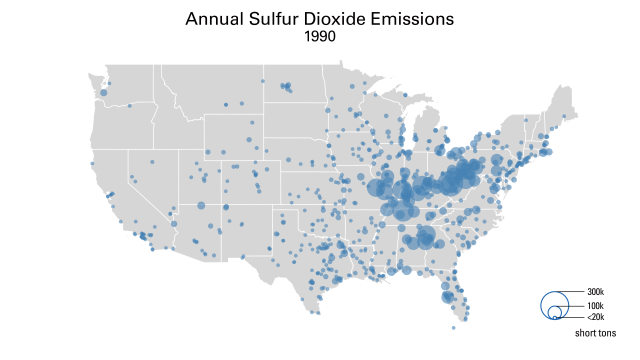
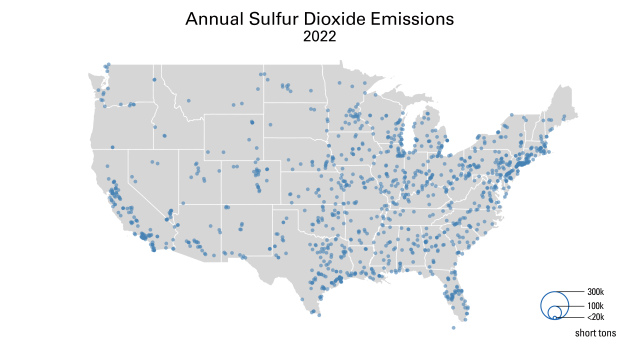
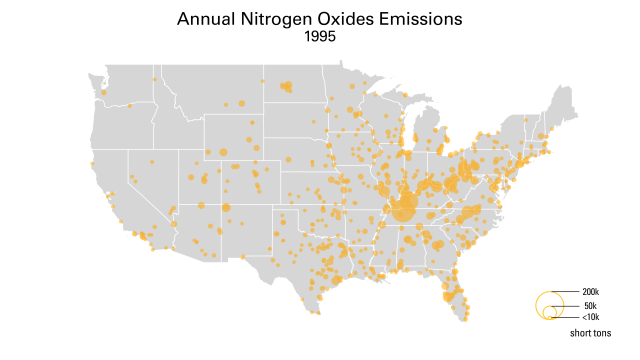
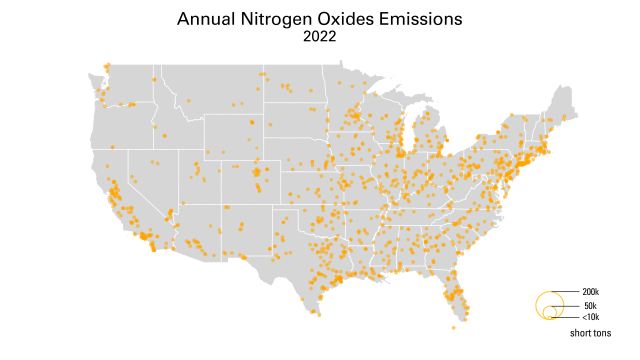
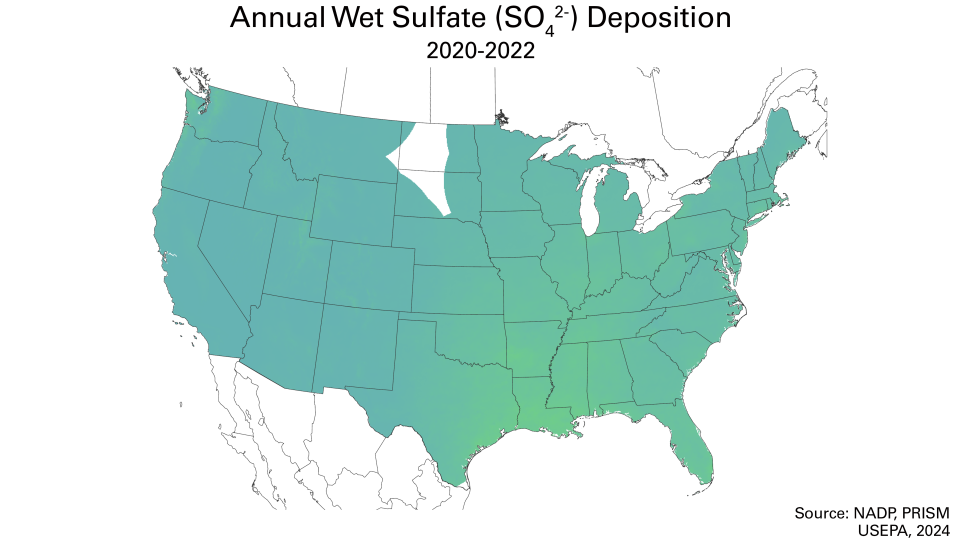
These emissions reductions have led to major decreases in acid rain nationwide. Wet sulfate deposition – a common indicator of acid rain – dropped by more than 70% between 1989-1991 and 2020-2022. Additional data and maps detailing deposition and ambient air pollution are available on the Clean Air Status and Trends Network (CASTNET) website.
Swipe left and right over the maps to see the changes before and after.
Next, learn more about the details of the Acid Rain Program.
Or, learn more about:
