GLIMPSE – A computational framework for supporting state-level environmental and energy planning
On this page:
- What is GLIMPSE?
- What are the benefits of GLIMPSE?
- Who should use GLIMPSE?
- What are the system requirements for using GLIMPSE?
- What's new in GLIMPSE v1.1?
- How do I get GLIMPSE?
- GLIMPSE Training
- GLIMPSE Users' Guide
- Related Presentations
- Related Publications
What is GLIMPSE?

GLIMPSE is a decision support tool being developed at EPA to assist EPA program offices, states, researchers and others with long-term environmental and energy planning. GLIMPSE is an acronym for the “GCAM Long-term Interactive Multi-Pollutant Scenario Evaluator,” where GCAM is the “Global Change Analysis Model.”
GCAM is an open source, publicly available human-Earth systems model that simulates the co-evolution of the economic, energy system, land use, and climate systems, including how this co-evolution is shaped by technologies, policies and other factors. Outputs from GCAM include the market shares of energy technologies and fuels, air pollutant and greenhouse gas emissions, policy costs, water use, and climate impacts. Work is ongoing to add air quality-related health impacts. GCAM development is led by the Joint Global Change Research Institute of Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
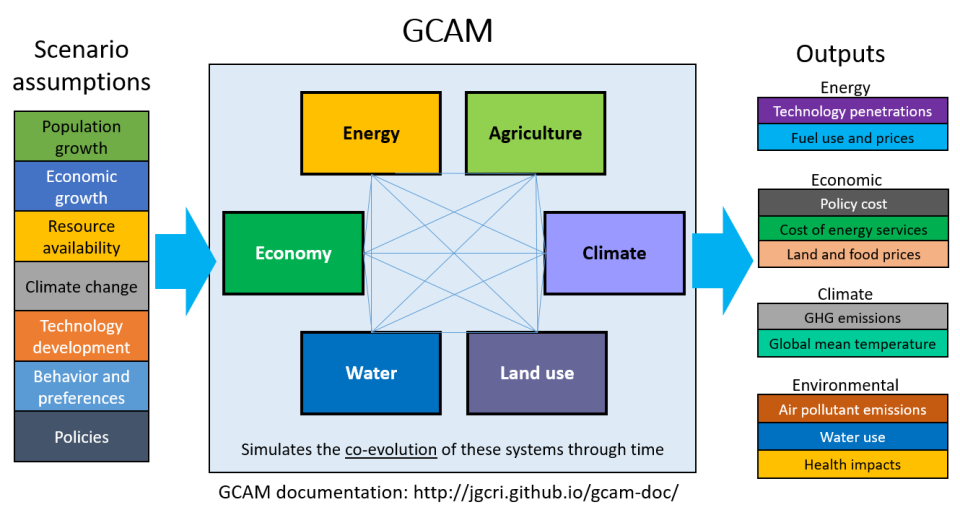
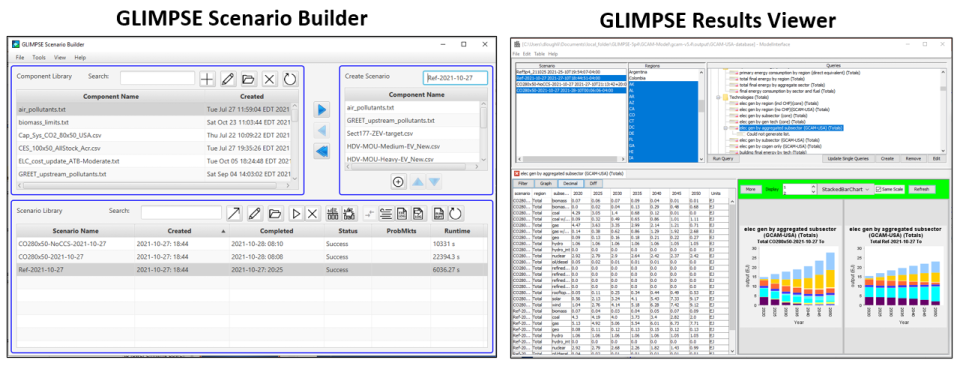
GLIMPSE acts as a graphical user interface for GCAM, bringing this complex and powerful model to a much broader set of users. GLIMPSE consists of the Scenario Builder and a Results Viewer. Using the Scenario Builder, decision-makers and analysts at the national, regional, and state levels can construct technology and policy scenarios, run the GCAM model, and track its execution. Users can create a rich set of scenarios by modifying technology assumptions and by representing a broad range of energy, air pollutant, and climate policies. Tools are available for diagnosing problems with scenarios and archiving scenarios such that they can be examined again in the future. The Results Viewer includes tools for comparing and visualizing the scenario results, as well as for highlighting the outputs that change the most from one scenario to another.
What are the benefits of GLIMPSE?
GLIMPSE’s greatest strengths are its ability to support decision-makers in:
- identifying the major sources of air pollutants and greenhouse gases (GHGs), both currently and over the coming decades;
- understanding how these emissions may be affected by new and emerging technologies; and,
- examining the impacts of policies from a holistic perspective, including the impacts across sectors, pollutants, and state boundaries.
User-Friendly: Users can specify many complex technology or policy scenarios in minutes. Visualization tools support the user in the interactive process of exploring the model’s results.
Fast: Once a scenario has been specified, model results are available within hours.
Flexible: Many of the assumptions about the future can be changed. For example, users could explore alternative assumptions about population and economic growth, technology availability, and future policies.
Comprehensive: By simulating the interactions among human and earth systems, GLIMPSE can identify important unintended consequences and other policy considerations that may not otherwise be apparent.
Multi-scale: Users can specify policies or examine energy technologies at the state, regional, or national level within the context of a global scenario.
Who should use GLIMPSE?
GLIMPSE software will be useful to federal, regional, and state policy analysts, energy and environmental planners, and faculty and students performing environmental and energy research.
Note: While GLIMPSE makes GCAM much easier to use, it is still a highly complex model that requires an investment of time and effort from the user to understand how it works and to interpret the results.
What are the system requirements for using GLIMPSE?
GLIMPSE currently runs on Windows computers. At least 16 GB of RAM is recommended, as well as 100 GB or more of free hard disk space. Future versions of GLIMPSE will be compatible with Linux and Apple operating systems.
What's new in GLIMPSE v1.1?
Compared to GLIMPSE v1.0, GLIMPSE v1.1 (released January 2024) includes the following major changes:
- GCAM updates:
- Transition to GCAM 7.0 from GCAM 5.4
- Learn more about the changes across GCAM versions.
- Enhancements to the GLIMPSE Scenario Builder:
- An updated Reference Case
- Improvements to the “New Scenario Component Creator” dialog, including providing filtering in technology selection and dollar-year conversions when specifying subsidies and taxes
- Enhancements to the GLIMPSE Model Interface:
- Reorganization of menus to improve usability
- New functionality to convert the units associated with model results
- Updated query file, including a new grouping that makes use of the unit conversions (e.g., reporting greenhouse gas emissions in units of mmCO2eq and electricity prices in $/kwh).
- Updates to the GLIMPSE Users’ Guide:
- Description of the new Reference Case
- Revised tutorials that reflect the transition to GCAM-USA 7.0 and the updated Reference Case and that also include an exercise investigating a Net-Zero decarbonization target
How do I get GLIMPSE?
Please contact Dan Loughlin ([email protected]) for access to GLIMPSE and to sign up for periodic trainings.
To keep apprised of GLIMPSE releases and trainings, you can subscribe to the glimpse-news listserv by sending an email to [email protected].
Technical Contacts:
GLIMPSE Training
GLIMPSE trainings from the Fall 2023 were recorded and can be viewed here:
- Training 1: Overview
- Training 2: Demonstration
- Training 3: Modeling GHG Reduction Measures
- Training 4: Multi-Pollutant Control Strategies
- Training 5: How GCAM Works
- Training 6: Linking GLIMPSE to other Modeling Frameworks
- Training 7: Special Topics
Email Dan Loughlin ([email protected]) if you are interested in participating in future trainings.
GLIMPSE Users' Guide
-
Users’ Guide for GLIMPSE: a Tool for Integrated Air-Climate-Energy Planning (pdf)
- Includes an overview of the GLIMPSE project, a description of the GLIMPSE Reference Scenario, a discussion of how GCAM works, and a five-part tutorial.
Related Presentations
- EPA Tools and Resources Webinar: This webinar, recorded September 22, 2022, provides an overview of a modeling framework called GLIMPSE that has the potential to explore a wide range of topics of interest to state air quality managers. Recording is approximately 46 minutes. Webinar slides are also available.
- EPA Air-Climate-Energy Research Webinar: This webinar, recorded August 15, 2023, provides an overview of the GLIMPSE and COMET tools, which support energy system modeling at the state and municipal resolution, respectively. The recording is 123 minutes. Webinar slides are also available.
Related Publications
- Evaluating long-term emission impacts of large-scale electric vehicle deployment in the US using a human-earth systems model (2021)
- Incorporating upstream emissions into electric sector nitrogen oxide reduction targets (2020)
- Air pollution control strategies directly limiting future health damages in the US (2020)
- State-level drivers of future fine particulate mortality in the United States (2019)
- Estimating environmental co-benefits of U.S. GHG reduction pathways using the GCAM-USA Integrated Assessment Model (2018)
- Projecting state-level air pollutant emissions using an integrated assessment model: GCAM-USA (2017)
