Distributed Structure-Searchable Toxicity (DSSTox) Database
Overview
EPA’s Distributed Structure-Searchable Toxicity (DSSTox) Database provides the chemical and chemistry underpinning for several publicly available applications including the Computational Toxicology Dashboard, the Ecotoxicity Knowlegebase, the Chemical Exposure Knowledgebase, and more.
The database currently exceeds one million substances which includes chemical lists of interest to EPA, other federal agencies, states, tribes, industry and other stakeholder groups.
DSSTox provides accurate linkages of chemical structures to source substance identifiers such as Chemical Abstract Service Registry Numbers – CAS RNs - and chemical names. This information allows high-quality association of the chemical to existing toxicity data, bioactivity data, experimental chemical property data and allows the use of this information in structure-based predictive modeling.
EPA continues to add high quality chemical and chemistry data to DSSTox and users can directly access the database. DSSTox provides a high-quality public chemical and chemistry resource.
Background
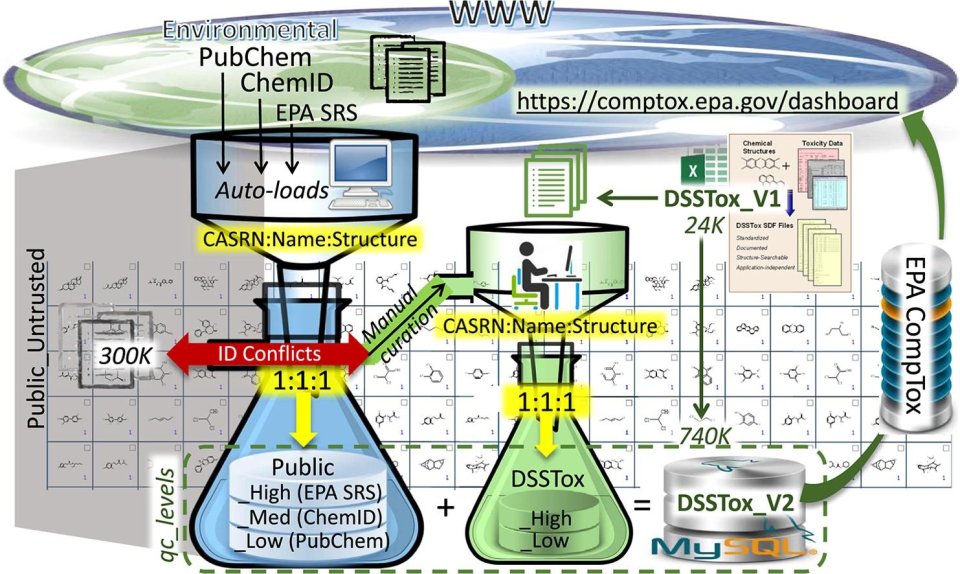
From its inception in 2004, DSSTox has focused on quality data curation efforts to resolve chemical identifier errors with the goal of ensuring accurate chemical structure alignment with data important to assessing chemical risk. Aligning chemical identifiers with accurate chemical structures are necessary inputs for more accurate chemical risk assessments.
DSSTox started as a manual curation of 7,000 chemicals and has expanded using auto-loads of portions of three public datasets: EPA’s Substance Registry Services (SRS), the National Library of Medicine’s ChemID, and PubChem. This process was constrained by a key requirement of uniquely mapped identifiers (i.e., CAS RN, name and structure) for each substance, rejecting content where any two identifiers were conflicted either within or across datasets. This rejected content highlighted the degree of conflicting, inaccurate substance-structure ID mappings in the public domain, ranging from 12% (within EPA SRS) to 49% (across ChemID and PubChem). Substances successfully added to DSSTox from each auto-load were assigned to one of five qc_levels, conveying curator confidence in each dataset.
