Adverse Outcome Pathway Database (AOP-DB)
On this page:
Basic Information

The same way you might piece together a jigsaw puzzle, scientists at the EPA are working hard to piece together information about the potential biological effects caused by chemicals in the environment. Their aim is to collect and connect biological information to create a fuller picture of how toxicity may be expressed in the body. The approach is helping to develop a consistent way for scientists worldwide to organize biological information-- a priority for the EPA. The science behind this approach is called Adverse Outcome Pathways, or “AOPs.”
What is an Adverse Outcome Pathway?
An Adverse Outcome Pathway (AOP) is a conceptual framework that portrays existing knowledge about biological events that could lead to an adverse outcome in health effects in human populations and ecosystems. This framework was designed for organizing these data, there by creating context to help better understand the bigger picture.
Currently, only a relatively small percentage of chemicals we are exposed to everyday have been evaluated in traditional toxicity tests. The good news is that we have massive amounts of information from various sources that can help us understand potential effects of the remaining chemicals in the market. And, we have the additional benefit of newer high-throughput screening methodologies which can be used to inform the potential effects of chemical exposure. But until AOPs, there was no consistent way to pull all this data together to understand it in context.
Who uses AOP's?
Potential users of this data may investigate specific molecular targets of an AOP, the relation of those gene/protein targets to other AOPs, cross-species, pathways, or disease-AOP relationships, or frequencies of AOP-related functional variants in particular populations, for example.
AOPs enable us to better use all existing information to evaluate “data poor” chemicals, even though they have not gone through the time intensive and expensive traditional toxicity tests. They allow scientists and decision-makers to access the latest scientific information to efficiently and effectively evaluate the safety of chemicals.
The EPA AOP-DB is an online database tool that combines different data types (AOP, gene, chemical, disease, or pathways) to help users characterize adverse outcomes of toxicological interest that are relevant to human health and the environment.
The AOP approach requires coordination and consistency among scientists worldwide to ensure their ability to inform chemical risk assessments and regulatory decisions. The EPA, in collaboration with the international scientific community, the European Joint Research Center, the US Army Corp of Engineers, the Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), and others are developing standardized approaches and tools to facilitate consistent development of AOPs.
These collaborations enable global “crowd sourcing” of information and establish common standards for mutual acceptance of data across borders.
Adverse Outcome Pathway Databases and Tools
Besides the AOP-DB there is also the AOP Knowledge Base, which is an internationally accessible and searchable web-based resource of AOP information. The AOP Knowledge Base, or AOP-KB, was designed to bring together comprehensive knowledge on how chemicals can result in adverse outcomes. This platform serves as a portal to share AOP tools and resources as they become publicly available.
The AOP-Wiki is another popular AOP resources, and is an interactive and virtual encyclopedia for AOP development intended to help the international scientific community recognize and agree on AOPs. The AOP-Wiki is maintained as part of the AOP Knowledge Base.
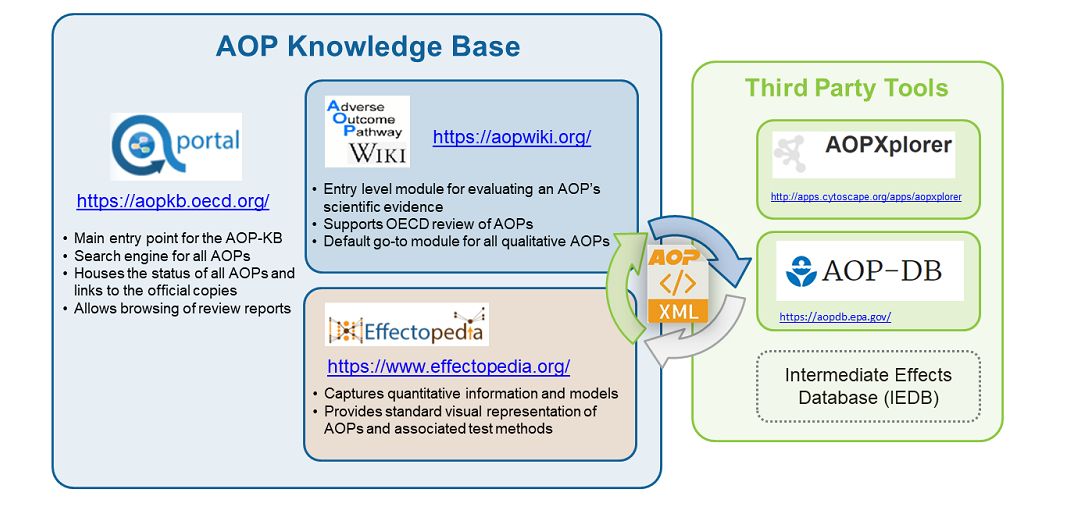
But the AOP-Wiki wasn't enough, so a team of EPA scientists began pulling together a collection of known data about chemicals, diseases and pathways, and constructed the AOP Database, or AOP-DB. This online application helped EPA to better characterize adverse outcomes of toxicological interest that are relevant to human health and the environment and present it in a format that decision makers could use to determine outcome.
At it's core, the AOP-DB application has been developed with the aim of integrating AOP molecular target information with other publicly available datasets from sources like the AOP-Wiki and AOP-KB to facilitate computational analyses of relevant information.
Learn about AOP-DB
How it works
An AOP maps out how a stressor (e.g. chemical) interacts within an organism to cause adverse effects. If the amount of the chemical is sufficient, then cells can be affected, which can then affect tissues (which are collections of cells), organs (which are collections of tissues), and, ultimately, the health of the organism or even the population as a whole.
By understanding the individual key events, one can better understand what the health outcome will be. Information used to develop AOPs can come from in vitro assays, animal studies and computational models. AOPs allow scientists to connect the in vitro results generated from rapid screening protocols to actual adverse outcomes.
Searching the AOP-DB
The main function of the AOP-DB application is searching. To query AOP-DB enter a keyword for any of the six parameters listed in table below and select the "Match By" boxes for the parameters of interest. Searching on any of the parameters will return a list of AOP's with matching terms or with an associated gene or stressor with a matching term.
Search Term Parameters
| Domain | Parameter | ID |
|---|---|---|
| AOP | AOP Name | AOP ID |
| Gene | Entrez ID | Disease ID |
| Stressor | Stressor Name | DTXS ID |
As you type a search term into AOP-DB, the interface will suggest match-able terms as input for any of the listed parameters. For example, query for AHR (aryl hydrocarbon receptor) yields AOP's with a matching name as well as two genes which are the AHR genes in humans and mice (entrez ID 196, Disease ID AHR; entrez ID 11622, Disease ID Ahr). Note that the suggestion was based on the Disease ID, not the description of the gene, and that for queries capitalization does not matter.
Associated with each AOP are four tables: genes, stressors, diseases, and biological pathways. Then each table can be filtered by any of the column values by entering a search term in the search box. The filtered results can then be exported as a CSV, Excel, or PDF file.
AOP-DB Tables & Queries
Gene Queries
As gene identifiers are not supplied in the AOP-Wiki directly, to create the AOP-gene link we mapped key event information within each AOP containing a protein ontology value to a corresponding gene identifier. Genes linked in this way can be viewed in the gene table.
Stressor Queries
Stressors are extracted directly from the AOP-Wiki. In cases where data was incomplete, incorrect, or too vague substances were manually mapped to individual chemical structures, to mixtures or to UVCB chemicals (Unknown or Variable Composition, Complex Reaction Products and Biological Materials).
Disease Queries
The associations between genes and human disease phenotypes in the AOP-DB are sourced from DisGeNET, which combines mined, curated, and inferred associations from ten sources for Mendelian, complex, environmental, and rare diseases as well as disease traits. Due to the redundancy of information across these ten data sources, a confidence score between 0 and 1 was calculated for each association based on the proportion of the sources that recognize that association. You can enter associated diseases using the inequality drop down and the numeric entry box.
History of AOP-DB
Below is a list of important milestones of the AOP-Database.
| Date | Milestone |
|---|---|
| Nov 2021 | EPA released the AOP-Database Application. |
| Oct 2021 | EPA submitted a paper about the AOP-DB to the Journal Frontiers in Toxicology. |
| Jul 2021 | The 2021 update of the EPA’s adverse outcome pathway database paper was published to Scientific Nature. |
| Sep 2020 | AOP-Database (DB) version 2 paper submitted to Nature Scientific Data. |
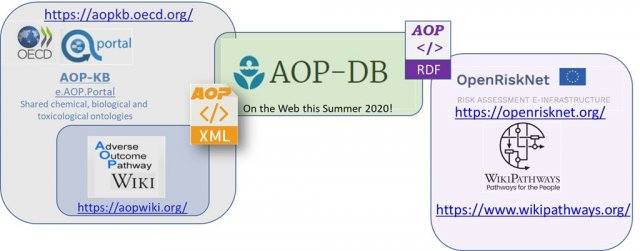
| Oct 2019 | AOP-Database RDF and SPARQL endpoint becomes available through OpenRiskNet. |
| Mar 2019 | AOP-Database implemented automated data pulls of AOPWiki XML. |
| Mar 2018 | AOP-Database mapped AOPwiki Stressor to ToxCast Assay information for the EPA Chemical Dashboard. |
| Jan 2018 | AOP-Database incorporates AOP-relevant SNP data and computational susceptibility workflows (Mortensen et al.,Mammalian Genome. Feb; 29(1-2):190-204. doi: 10.1007/s00335-018-9738-7. Epub 2018 Feb 23.) |
| Jan 2018 | AOP-Database version 1 paper published (Pittman et al. TAAP. Mar 15; 343:71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Feb 14.) |
| Mar 2016 | EPA created the AOPWiki to support the crowdsourcing of adverse outcome pathway information. |
| Oct 2015 | AOP-Database was developed as an internal application to help EPA staff organize and interpret the AOP-Wiki Data. |
For assistance/questions please use the AOP-DB Contact Us page. For general Health Research questions, separate from the AOP-DB, please use the link below.
Resources
EPA Reports
Download the AOP-DB Manual
EPA References & Materials
- EPA Published Posters, Presentations, and Articles Related to Adverse Outcome Pathways (AOPs)
- CompTox Chemicals Dashboard - AOP-DB Stressor
- AOP-DB SPARQL Endpoint
- AOP-Wiki
- OECD AOP-KB Knowledge Base
- OECD Webinars on Adverse Outcome Pathways
- SeqAPASS
- Adverse Outcome Pathways Fact Sheet
- Adverse Outcome Pathways Research Brief
Journal Articles
- Mortensen, H.M., Chamberlin, J., Joubert, B., Angrish, M, Sipes, N., Lee, J.S., Euling, S.Y. (2018) Leveraging human genetic and adverse outcome pathway (AOP) data to inform susceptibility in human health risk assessment. Mammalian Genome Feb;29(1-2):190-204. doi: 10.1007/s00335-018-9738-7. Epub 2018 Feb 23.
-
Mortensen, H.M. Martens, M. Senn, J. Levey, T., Evelo, C.T., Willighagen, E.L., Exner, T. (2022) The AOP-DB RDF: Applying FAIR Principles to the Semantic Integration of AOP Data Using the Research Description Framework Feb 2022; doi: 10.3389/ftox.2022.803983. Front Technology 2022 Feb 14.
-
Mortensen, H.M., Senn, J., Levey, T., Langley, P., Williams, A.J. (2021) The 2021 update of the EPA’s adverse outcome pathway database. Scientific Data 8, 169 (2021). doi: 10.1038/s41597-021-00962-3, Aug 2021.
-
Pittman, M.E., Edwards, S.W., Ives, C., Mortensen, H.M. (2018) AOP-DB: A database resource for the exploration of Adverse Outcome Pathways through integrated association networks. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology Mar 15; 343:71-83. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.02.006. Epub 2018 Feb 14.
-
Oki, N.O., Nelms, M.D., Bell, SM., Mortensen, H.M., Edwards, S.W. (2016) Accelerating Adverse Outcome Pathway Development Using Publically Available Data Sources. Current Environmental Health Reports, Mechanisms of Toxicity Section: 1-11.
Datasets
Because AOP-DB draws data from a number of sources each with release and update schedules independent of one another, AOP-DB updates it's records on a quarterly basis. Updates are conducted by scripted routines that ensure data integrity and consistency across all tables, remove duplicate records, and perform sample queries with known expected results to test the coherence and delity of the database.
| Biological Category | Data Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Gene | NCBI Gene | This source supplies all NCBI entrez genes in the gene info table with associated gene information such as name, symbol, location, etc. |
| Gene | STRING | This source gives protein-protein interaction data for the gene-interactions table. Each record from these networks is stored with an entrez1, entrez2, and an interaction score. |
| Taxonomy & Orthology | NCBI Taxonomy | All taxa available from NCBI, including nomenclature info and divisions. This data is used to fill the species info. |
| Taxonomy & Orthology | Homologene | Constructs and stores putative homology groups and contributes to ortho group number, tax IDs, and entrez IDs to the homology gene table. |
| Taxonomy & Orthology | KEGG Orthology | This database of functional orthologs contributes to ortho group IDs, tax IDs, and entrez IDs describing an orthologous group to the homology gene table. |
| Taxonomy & Orthology | metaPhOrs | This database of phylogeny based orthologs contributes ortho group IDs, taxonomy IDs, and entrez IDs to the homology gene table, describing orthologous groups. |
| AOP | AOP-wiki | This is a collaborative set of AOPs regularly updated with new details or new Adverse Outcome Pathways. This source contributes to the central AOP info tables and the AOP gene tables, supplying AOP names, key events, descriptions, and information used to map key events to genes. |
| Chemical | CTD | This source is a manually curated database of chemical information, including many modules. The module of interest for the AOP-DB is the chemical gene interactions module, which contributes chemical names and ids to chemical info, as well as the chemical gene interactions with contextual information to the chemical gene table. |
| Chemical | AOP-wiki | In addition to being the source of AOPs for the AOP-DB, this source also adds chemical stressors related to the MIE of each AOP. This data contributes chemical names, as well is DTXS IDs, CASRNs, or other chemical IDs when available. |
| Chemical | ToxCast | This is a collection of high-throughput screening assays for chemicals that contributes assay identification information and assay context information as well as gene target information in the form of entrez IDs. |
| Pathway | KEGG Pathways | This source is a collection of biological molecular interaction pathways that supplies entrez IDs and pathway names and IDs, linking gene components to the pathways in which they are involved. |
| Pathway | Reactome | This curated and peer-reviewed source of molecular pathways supplies entrez IDs and their linked pathways to the pathway gene table of the AOP-DB. |
| Pathway | ConcensusPathDB | This source brings together pathway and interaction data from 32 public resources and supplies entrez IDs and pathway IDs that link genes to biological pathways for the pathway gene table. |
| Disease | DisGeNET | This database compiles different data, both curated and inferred from models, and supplies multiple downloadable tables relating genes and variants to the diseases in the database. The AOP-DB uses DisGeNET's gene-disease association table, adding all fields to the disease-gene table. These include disease name and ID, entrez ID, and a score for the association based on its sources. |
| Ontology | NCBI Gene | In addition to being a source of taxonomy info and gene info, NCBI Gene supplies gene ontology information. This supplies gene ontology terms and any related entrez IDs to the GO gene table. |
| Tissues | HumanBase | This API is used to pull tissue specific gene interaction network from HumanBase. The data imported into the tissue networks table in the AOP-DB include entrez1 and entrez2 fields to construct edges, as well as a probability score indicating the strength of the modeled gene interaction. |
| Haplotypes | 1000 Genomes | This is a collection of variant data for individuals from a multitude of populations. This source contributes snp frequencies for each function snp in the snps table for each of five 1000 Genomes major populations. |
| Haplotypes | Ensemble | This API, allowing access to ensemble's gene and variant information, is used to get genotype data for each individual sample from the 1000 Genomes project. These data are used to construct haplotypes for each AOP and find differences in haplotype frequencies within and between populationshttps://gaftp.epa.gov/EPADataCommons/. |
| Haplotypes | GWAS Catalog | This is a source used to filter SNPs into snps of interest for variant analysis in different populations. Functional snps are specifically targeted. It, along with GTEx, supplies refsnp ids for these variants as well as contextual information. |
| Haplotypes | This is a source used to filter SNPs into snps of interest for variant analysis in different populations. Functional snps are specifially targeted. It, along with GWAS Catalog, supplies refsnp IDs for these variants as well as contextual information. |
The AOP-DB data frame with all corresponding table data (from the sources listed above) has been uploaded to the U.S. EPA Environmental Data gateway at EPA Data Commons.
- They can be accessed from EPADataCommons/ORD/AOP-DB, and on the USEPA ScienceHub data repository (DOI: 10.23719/1522396).
