Retrospective Case Study in Wise County, Texas
Case Study Background
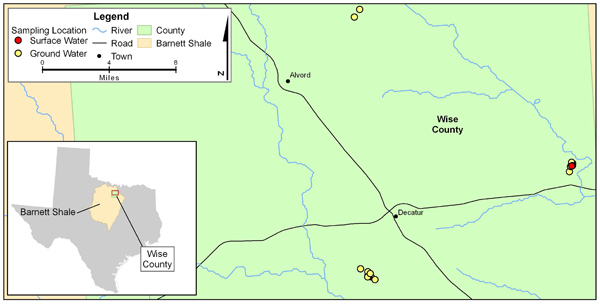
EPA conducted a retrospective case study in Wise County, Texas to investigate reported instances of contamination of drinking water resources in areas where hydraulic fracturing activities occurred. This case study provided valuable insight into vulnerabilities and potential pathways for impacts to drinking water resources from hydraulic fracturing activities such as surface activities, and well construction and integrity.
- Report: Retrospective Case Study in Wise County, Texas (PDF)
- Fact Sheet: Wise County, Texas Retrospective Case Study
Key Findings
-
For two of the study locations there were no impacts to ground water based on the comparisons made between the study data and historical water quality data.
- In the third study area, two domestic wells were identified as impacted. Based on the screening of potential sources of impacts, formation brines (brines associated with specific geological formations) were the only source that was consistent with the observed impacts to two of the study wells.
- A third well that is not being used for drinking water indicated brines and landfill leachate as the potential source for the observed impact in the study area.
State Activities at the Case Study Location
Texas has taken follow-up actions to protect water resources and to identify the sources of the potential impacts near the two impacted domestic wells.
Sampling Activities
EPA completed five rounds of water sampling from September 2011 to May 2013. Water samples were collected from domestic wells, surface water, and production wells in three areas where homeowners expressed concerns regarding potential adverse impacts to their well water as a result of drilling and processes related in to hydraulic fracturing of nearby wells. The majority of the domestic well samples (15 of 16) were from the Trinity aquifer which is the primary source of drinking water in Wise County.
Data Reports