Basic Information about Electronics Stewardship
According to a 2013 report by the Consumer Electronics Association, the average American household uses about 28 electronic products such as personal computers, mobile phones, televisions and electronic readers (e-readers). With an ever increasing supply of new electronic gadgets, EPA's Facts and Figures about Materials, Waste and Recycling show that Americans generated 2.7 million tons of consumer electronics goods in 2018, representing less than one percent of all municipal solid waste generation.
On this page:
- Sustainable Approaches for Every Stage of the Electronics Life Cycle
- Sustainable Electronics Management
- Benefits of Electronics Stewardship
- Related Information
Sustainable Approaches for Every Stage of the Electronics Life Cycle
Sustainably managing electronics by reducing the amount of materials used, increasing reuse, refurbishing and extending the life of products, and recycling electronics can help reduce the amount of waste that needs to be managed domestically and globally. Examining a product’s entire life cycle can uncover new opportunities to reduce environmental impacts, conserve resources, and reduce costs.
The graphic below shows each life cycle stage, which are described in more depth under the graphic. Some electronics manufacturers have adopted innovative approaches to ensure electronic products are sustainably sourced, designed, and managed throughout their life cycles. The companies mentioned here have received awards from EPA’s Sustainable Materials Management (SMM) Electronics Challenge for these practices.
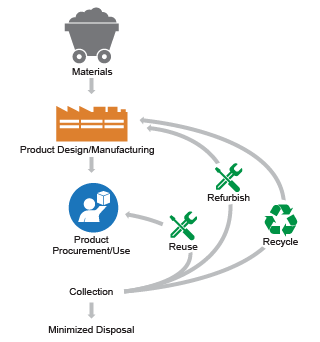
A circular life cycle of electronic products includes the following stages:
Sourcing Materials
Materials such as iron, gold, aluminum, palladium, platinum, lithium, copper, and plastics play crucial roles in the high-tech electronics products that affect our daily lives. These materials are extracted from the earth, transported, processed, refined, and incorporated into products. These activities use large amounts of energy and produce greenhouse gas emissions, pollute the environment, and deplete our natural resources. Reducing materials can save natural resources, conserve energy, and reduce pollution.
Product Design and Manufacturing
Designing and manufacturing electronics with the environment in mind is critical for developing more sustainable products. Source reduction, also known as waste prevention, is important in design and manufacturing, as electronics that have less impact on human health and the environment often use less materials overall, use more recycled materials, are more durable, and are recyclable.
Product Procurement and Use
A first step in using electronics sustainably involves educating consumers about sustainable purchasing choices. Learn about innovative approaches for product procurement and use.
Manufacturers have a responsibility to create durable, long-lasting, reusable, and recyclable products, but consumers also play a significant role in maintaining their electronics.
Collection
Community drop-off points, certain retailers, and manufacturers through mail-in, take-back, and warranty programs collect electronics. These collection entities either send reusable electronics to recovery facilities to be reused, refurbished, and resold, or to recycling facilities to be sorted, cleaned, and processed into materials that can be used again in manufacturing. After collection, reusable electronics are refurbished and resold, and recyclables are sent to recycling facilities to be sorted, cleaned, and processed into materials that can be used again in manufacturing.
Reuse and Refurbishing
Refurbished electronics are electronics that have been updated and repaired for resale. Reusing electronics extends product life spans and contributes to the source reduction of raw materials.
Recycling
Recycling includes sorting, dismantling, mechanically separating, and recovering valuable materials. Recycling used electronics can yield materials (e.g., gold, copper, glass, aluminum) that can be returned to the supply chain to be reused, reducing raw materials used and the need for disposal of the used electronics.
Sustainable Electronics Management
Electronic devices and technologies continue to advance and increase in number. These technologies have become critical to our way of life and to our growing economy. With these technologies, however, comes the increasing challenge of protecting human health and the environment from the potentially harmful effects associated with their improper handling and disposal.
A long-term sustainable approach towards electronics stewardship is necessary both at work and at home. With the prevalence of electronics in mind, the federal government is committed to being a responsible consumer of electronics and a leader of electronics stewardship in the United States. Sustainable electronics management involves the following practices:
Reusing and donating electronics
Preventing waste in the first place is preferable to any waste management option, including recycling. Donating used (but still operating) electronics for reuse extends the lives of valuable products and keeps them out of the waste stream for a longer period of time.
Recycling electronics
If donation for reuse or repair is not a viable option, households and business can send their used electronics for recycling.
Buying green
Environmentally responsible electronics use involves not only proper end-of-life disposition of obsolete equipment, but also purchasing new equipment that has been designed with environmentally preferable attributes.
Benefits of Electronics Stewardship
Increasing sustainable electronics management efforts can create green jobs, lead to more productive reuse of valuable materials, increase the value of American exports, and support a vibrant American recycling and refurbishing industry. If done properly, the United States can increase its domestic recycling efforts, reduce harm from exports of electronics waste (e-waste) being handled unsafely in developing countries, strengthen domestic and international markets for viable and functional used electronic products, and prevent health and environmental threats at home and abroad.
Recycling electronics helps reduce pollution that would be generated while manufacturing a new product and the need to extract valuable and limited virgin resources. Electronic recycling also reduces the energy used in new product manufacturing.
Donating electronics allows schools, nonprofit organizations and lower-income families to obtain equipment that they otherwise could not afford. Businesses can also take advantage of tax incentives for donated computer equipment.
Green electronics contain fewer toxic constituents. The use of recycled materials in new products promotes the following benefits:
- More energy efficient (e.g., showing the Energy Star label).
- More easily upgraded or disassembled.
- Use minimal packaging.
- Offers leasing or takeback options.
- Meets performance criteria and shows they are more environmentally preferable.
Related Information
A Sustainable Materials Management approach seeks to:
- Use materials in the most productive way with an emphasis on using less.
- Reduce toxic chemicals and environmental impacts throughout the material lifecycle.
- Assure we have sufficient resources to meet today’s needs and those of the future.
Information on materials used in electronics are available in the following U.S. Geological Survey publications:
