EPA EcoBox Tools by Exposure Pathways - Soil
Overview

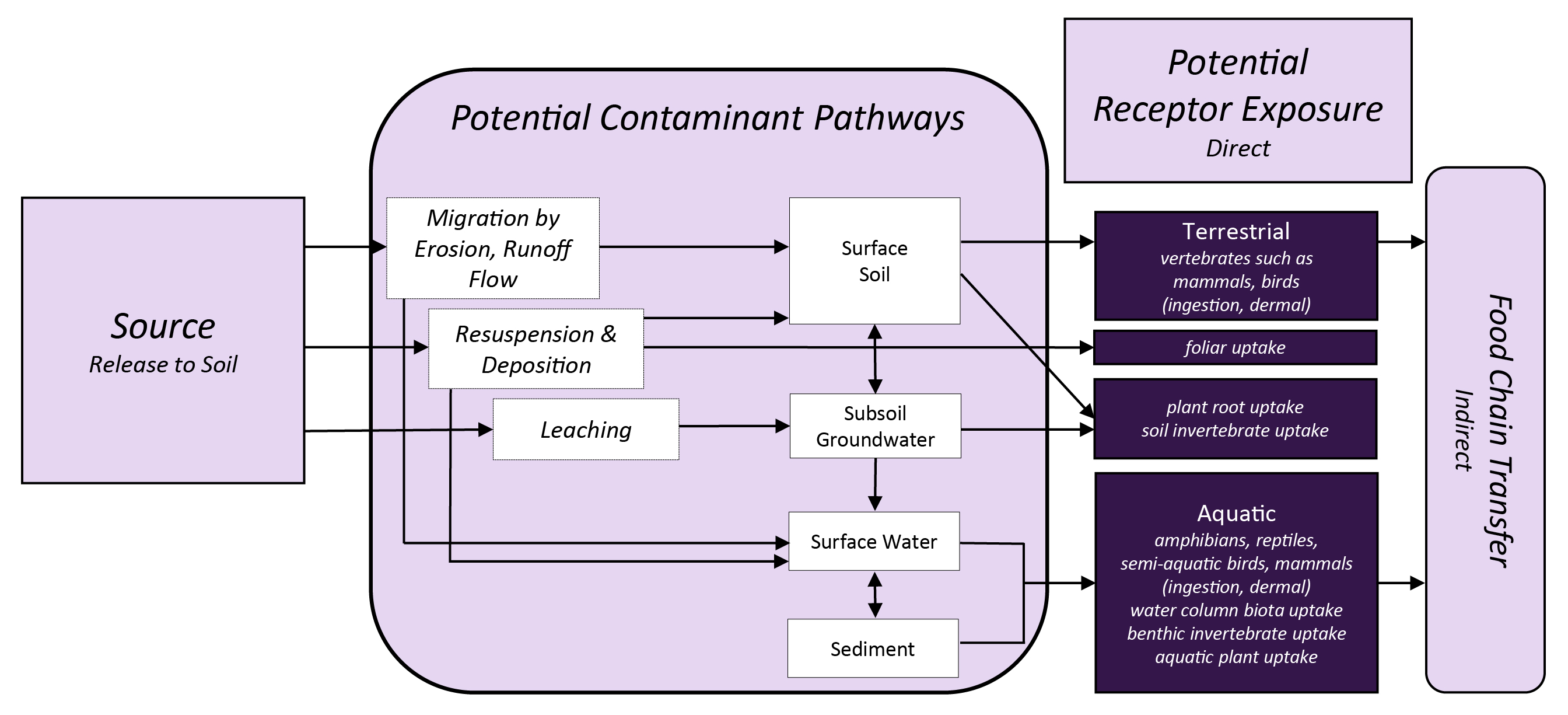
Contaminated soil or dust particles can be deposited onto plant surfaces. A stressor released directly to soil could migrate by erosion and runoff flow to nearby soil or adjacent aquatic systems. Contaminants in surface soil can leach to subsoil and groundwater, and contaminated groundwater could discharge to a surface water body.
Exposure to contaminants in soil can occur from direct contact (e.g., ingestion, dermal) or indirect from transfer and subsequent contact with other media (e.g., uptake from soil into vegetation and subsequent ingestion). For example:
- Contaminated soil or dust particles on plant surfaces can become translocated to different plant tissues.
- Plants growing in contaminated soil can take up the stressors from soil pore water through their roots.
- Stressors in vegetation or soil may be consumed by grazing or foraging animals that bioaccumulateBioaccumulation is the general term describing a process by which chemicals are taken up by a plant or animal either directly from exposure to a contaminated medium (soil, sediment, water) or by eating food containing the chemical. Related terms are bioconcentration which chemicals are absorbed by an animal or plant to levels higher than the surrounding environment; and biomagnification, in which chemical levels in plants or animals increase from transfer through the food web (e.g., predators have greater concentrations of a particular chemical than their prey). the stressors in their tissues.
- Stressors in soil could also be taken up by soil invertebrates and soil microbes or consumed incidentally by small burrowing mammals and birds.
- Aquatic organisms could be exposed to stressors in the water column or deposited to sediments. Semi-aquatic and terrestrial animals could be exposed to the water while swimming or drinking.
Indirect exposure occurs for animals that consume contaminated food and these contaminants can be transferred up the food chainA food chain is formed as one organism eats another. A food web is a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains, in which each organism supplies energy to another life form..
The diagram below illustrates relationships between potential exposure pathways and potential ecological receptors after a source releases a stressor to soil.
Resources are provided below to assess exposure to ecological receptors that occurs via soil.
Tools
Resources are provided below to assess exposure to ecological receptors that occurs via soil.